Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) Drugs Market Size & Industry Outlook
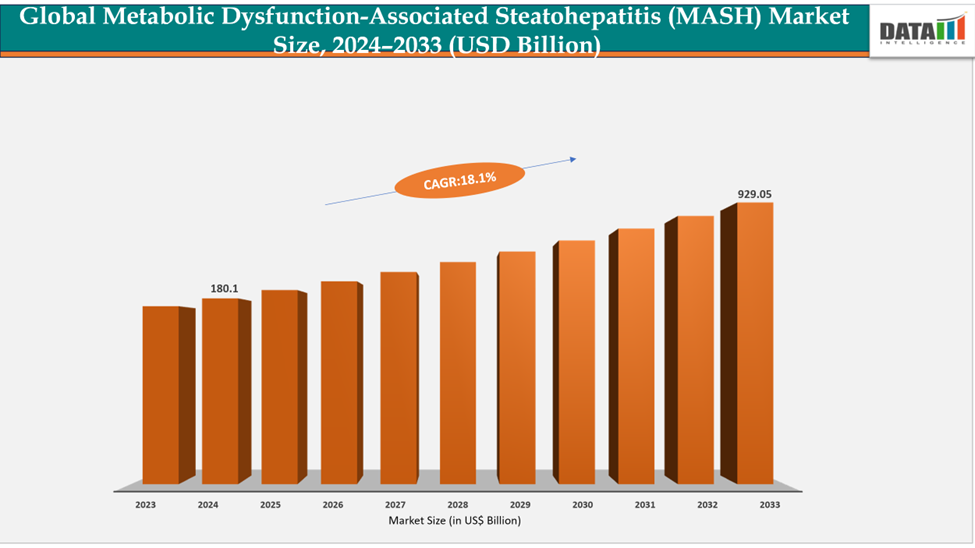
The global metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) market size reached US$ 180.1 million in 2024 is expected to reach US$ 929.05 million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 18.1% during the forecast period 2025-2033. The global obesity rate rising continuously with approximately 2.3 billion children and adults are living with overweight or obese, creating a direct risk for MASH. Type 2 diabetes is another significant risk factor, with an estimated 462 million individuals many of whom are at high risk of developing MASH.
Currently, there are only 2 FDA-approved drugs for MASH, which are Rezdiffra (resmetirom) and WEGOVY (semaglutide), making these diseases an area of high unmet medical need, which drives company focus for new therapies.
Expansion of these FDA-approved drugs into major regions is further driving the market growth. For instance, in August 2025, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Inc. announced that the European Commission (EC) granted conditional marketing authorization for Rezdiffra (resmetirom) for the treatment of adults with noncirrhotic MASH with moderate to advanced liver fibrosis. Rezdiffra is now the first and only approved therapy in the European Union (EU) for the treatment of MASH.
There are several promising therapies in the pipeline targeting MASH. Continued clinical trials and successful market approval of these pipeline treatments will likely propel the growth of the market. For instance, in October 2024, Boehringer Ingelheim announced that survodutide (BI 456906), a dual glucagon/GLP-1 receptor agonist, has been designated as a Breakthrough Therapy by the United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the treatment of adults with non-cirrhotic metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) and moderate or advanced fibrosis.
Key Highlights
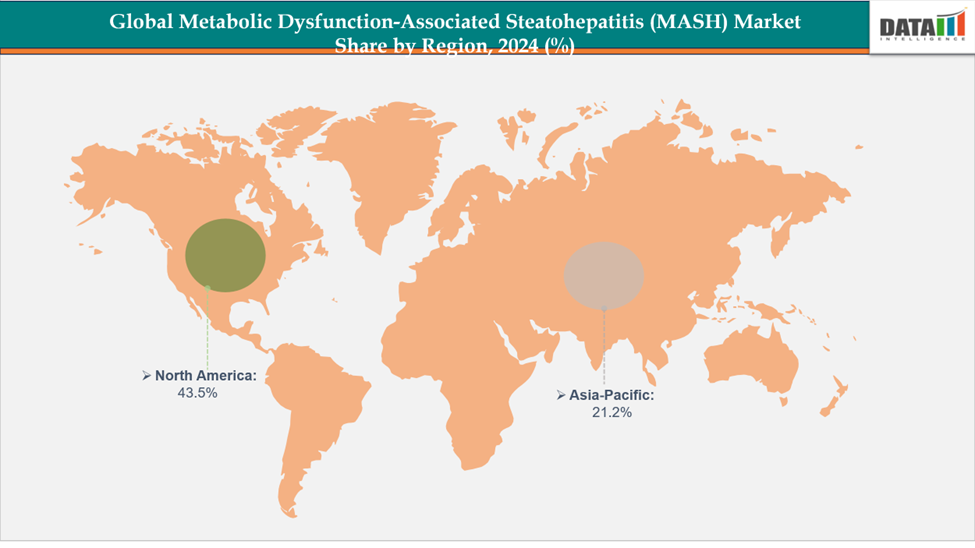
- North America dominates the metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) market with the largest revenue share of 43.5% in 2024.
- The Asia Pacific is the fastest-growing region and is expected to grow at the fastest CAGR of 8.1% over the forecast period.
- Based on disease stage, stage 4 segment led the market with the largest revenue share of 45.1% in 2024.
- The major market players in the Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) market includes Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Inc, Novo Nordisk and among others.
Market Dynamics
Drivers: Growing prevalence of dental disorders driving the Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) market growth
The rising prevalence of underlying conditions such as obesity, type 2 diabetes and other metabolic syndrome is a key factor driving the growth of the MASH market. These conditions contribute significantly to the development of liver diseases, particularly MASH, which are increasingly recognized as public health concerns globally.
For instance, according to the World Obesity Federation estimates, more than 1 Million people globally are living with obesity, 880 million are adults and 159 million are children and adolescents aged 5-19 years. Obesity is a major risk factor for both MASH and MASH. The global obesity rate has surged over the past few decades, contributing directly to an increase in liver-related diseases.
In obese individuals, excess fat accumulation in the liver (known as NAFLD, Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) can progress to more severe stages such as MASH. About 20-30% of people with NAFLD will eventually develop MASH, increasing the demand for effective treatments.
Restraints: Limited number of approved drugs are hampering the growth of the Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) market
One of the major challenges in the MASH market is the limited availability of approved therapies. Despite significant R&D efforts, no universally approved drugs currently exist for MASH, forcing physicians to rely on off-label treatments targeting associated metabolic conditions such as diabetes or obesity. This lack of approved options slows market growth and delays widespread clinical adoption. Moreover, the complex pathophysiology of MASH, involving metabolic, inflammatory, and fibrotic pathways, makes drug development highly challenging, leading to high trial failure rates and extended approval timelines.
For more details on this report – Request for Sample
Segmentation Analysis
The global Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) market is segmented based on disease stage, medication, route of administration and region.
Disease Stage The Stage 4 from disease stage segment to dominate the Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) market with a 45.1% share in 2024
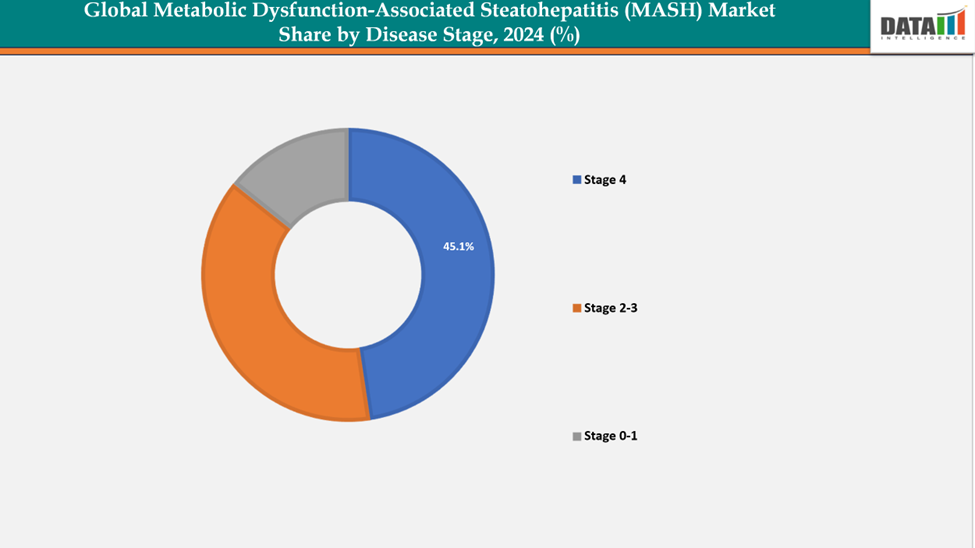
Cirrhosis (fibrosis stage 4), the liver exhibits extensive scarring that changes its shape. Despite this severe damage, the liver can still function and may have the capacity to repair some of the injuries. However, if excessive scarring occurs, the liver's ability to carry out its essential functions may be impaired. This stage represents a critical condition that requires continuous management to prevent further deterioration and related complications.
At this stage "3.5 million compensated and decompensated cirrhosis F4+" refers to the estimated number of individuals diagnosed with cirrhosis at stage F4, indicating severe liver damage and scarring. This group includes those with compensated cirrhosis, where the liver still functions adequately despite significant scarring, and decompensated cirrhosis, where the liver can no longer maintain its functions, leading to serious complications such as fluid accumulation (ascites), jaundice, or hepatic encephalopathy. This statistic highlights a major public health concern, as it points to a substantial population at risk for severe health complications and emphasizes the urgent need for effective management and treatment strategies.
Around "25 thousand annual cases among MASLD population hepatocellular carcinoma" refers to the estimated number of new hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) cases arising each year within the population affected by metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease (MASLD). This statistic underscores the increasing incidence of HCC associated with MASLD, which is becoming recognized as a significant risk factor for liver cancer. As the prevalence of MASLD continues to rise, so does the likelihood of developing HCC, highlighting the urgent need for enhanced screening and management strategies for individuals at risk.
Route of Administration: The oral segment is estimated to have a 41.1% of the Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) market share in 2024
The oral segment is gaining strong traction in the MASH market due to its patient-friendly administration, better compliance, and cost-effectiveness compared to injectable therapies. The growing preference for convenient, non-invasive treatment options among patients with chronic metabolic conditions is further accelerating demand. Additionally, several leading pharmaceutical companies are focusing on developing oral small-molecule therapies, such as pan-PPAR agonists and thyroid hormone receptor-beta agonists, which have shown promising efficacy in clinical trials. This trend underscores the shift toward simplified, long-term management approaches for MASH.
Geographical Analysis
North America dominates the global Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) market with a 43.5% in 2024
The high prevalence of metabolic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes and hypertension in North America is a major driver of the MASH market. These conditions are significant risk factors for NAFLD (Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease) and MASH. For instance, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC), in the United States, the prevalence of obesity in adults was 40.3%, with no significant differences between men and women. More than 38 million Americans have diabetes (about 1 in 10), and about 90% to 95% of them have type 2 diabetes. Nearly 1 out of 2 adults in the United States has hypertension (116 million).
Rising FDA approvals in the United States is also accelerating the market growth. For instance, in March 2024, Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Inc. cleared the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) accelerated approval for Rezdiffra (resmetirom) in conjunction with diet and exercise for the treatment of adults with noncirrhotic MASH with moderate to advanced liver fibrosis (consistent with stages F2 to F3 fibrosis).
Similarly, in August 2025, Novo Nordisk received the US Food and Drug Administration’s (FDA) accelerated approval for Wegovy (semaglutide 2.4mg) to treat noncirrhotic metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) in adults with moderate to advanced liver fibrosis. The drug is approved for use alongside a reduced-calorie diet and increased physical activity.
Europe is the second region after North America which is expected to dominate the global Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) market with a 34.5% in 2024
Europe is witnessing growing momentum in the MASH market due to increasing obesity and type 2 diabetes prevalence, which are key risk factors for metabolic liver diseases. Governments and healthcare organizations are prioritizing early diagnosis and patient awareness initiatives, driving clinical adoption. Moreover, active participation in clinical trials and collaborations between biotech and pharma companies are accelerating drug development across the region.
Germany stands out as a major contributor within Europe, driven by strong research infrastructure, high healthcare spending, and a robust network of academic–industry collaborations. The country’s emphasis on precision medicine and biomarker-based diagnosis supports the development of targeted MASH therapies. Additionally, Germany’s regulatory efficiency and growing clinical trial activity make it a preferred destination for global biotech firms focusing on MASH innovation.
The Asia Pacific region is the fastest-growing region in the global Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) market, with a CAGR of 8.1% in 2024
The Asia Pacific region is emerging as a key growth hub in the Global MASH market, driven by the rising prevalence of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and sedentary lifestyles, which are major risk factors for metabolic liver diseases. Countries like China, India, and Japan are witnessing an alarming increase in fatty liver cases due to changing dietary habits and urbanization. Governments and healthcare systems are investing in early screening and non-invasive diagnostic tools such as transient elastography to improve disease detection rates.
Japan stands out in the Asia Pacific region due to its advanced healthcare infrastructure and progressive regulatory environment that supports innovative drug development in liver diseases. The government’s focus on tackling lifestyle-related diseases and the rising incidence of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD) and MASH among aging populations are fueling market expansion.
For instance, in February 2025, Inventiva and Hepalys Pharma have initiated their clinical development program in Japan, marking a key milestone in their collaboration to advance innovative treatments for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) in Asian markets. The program began with the first Japanese participant dosed in a Phase 1 clinical trial of lanifibranor, a novel pan-PPAR agonist developed by Inventiva, aimed at addressing the unmet therapeutic needs in MASH.
Competitive Landscape
Top companies in the metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) market include Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Inc, Novo Nordisk among others.
Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Inc:- Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Inc. plays a pivotal role in shaping the Global Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) market as the first company to secure FDA approval for a MASH-specific therapy. Its breakthrough drug, resmetirom (brand name Rezdiffra™), a thyroid hormone receptor-β (THR-β) agonist, addresses the root causes of MASH by reducing liver fat, inflammation, and fibrosis. Following strong results from its MAESTRO-NASH Phase 3 trial, the FDA granted accelerated approval in March 2024 for adults with non-cirrhotic MASH with moderate to advanced fibrosis (F2–F3), without requiring liver biopsy—marking a major regulatory milestone in this previously untreatable condition.
Market Scope
| Metrics | Details | |
| CAGR | 18.1% | |
| Market Size Available for Years | 2022-2033 | |
| Estimation Forecast Period | 2025-2033 | |
| Revenue Units | Value (US$ Mn) | |
| Segments Covered | Disease Stage | Intraoral X-ray, Extraoral X-ray, Imaging Software, Others |
| Medication | 2D Digital Radiography, 3D CBCT, Optical/impression scanners, Digital sensors, Hybrid Systems | |
| Route of Administration | Endodontics, Implantology, Orthodontics, Oral & Maxillofacial Surgery, Others | |
| Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America and the Middle East & Africa | |
The global Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) market report delivers a detailed analysis with 62 key tables, more than 57 visually impactful figures, and 159 pages of expert insights, providing a complete view of the market landscape.
Suggested Reports
- North America Metabolic Dysfunction Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH) Treatment Market
- Metabolic Disorders Therapeutics Market
For more pharmaceuticals-related reports, please click here