Hemophilia B, also known as Christmas disease, is a rare genetic bleeding disorder caused by a deficiency or dysfunction of clotting factor IX (FIX). Traditionally managed with plasma-derived or recombinant FIX concentrates, the landscape of Hemophilia B treatment has expanded dramatically in recent years. With the emergence of gene therapy, siRNA-based treatments, and inhibitors of the tissue factor pathway, patients and clinicians now have a broader arsenal of options that offer improved efficacy, reduced infusion frequency, and even the potential for long-term correction.
With over a dozen companies leading both marketed and investigational products, the horizon for Hemophilia B care continues to expand in 2025.
This blog explores the current and emerging treatments, covering everything from recombinant FIX to gene editing.
Established Treatments: Recombinant and Plasma-Derived FIX
Recombinant Factor IX Concentrates
Recombinant FIX products are lab-engineered proteins that replace the missing clotting factor without relying on human plasma, reducing the risk of pathogen transmission. Several pharmaceutical giants have developed next-generation recombinant FIX therapies with extended half-lives for less frequent infusions.
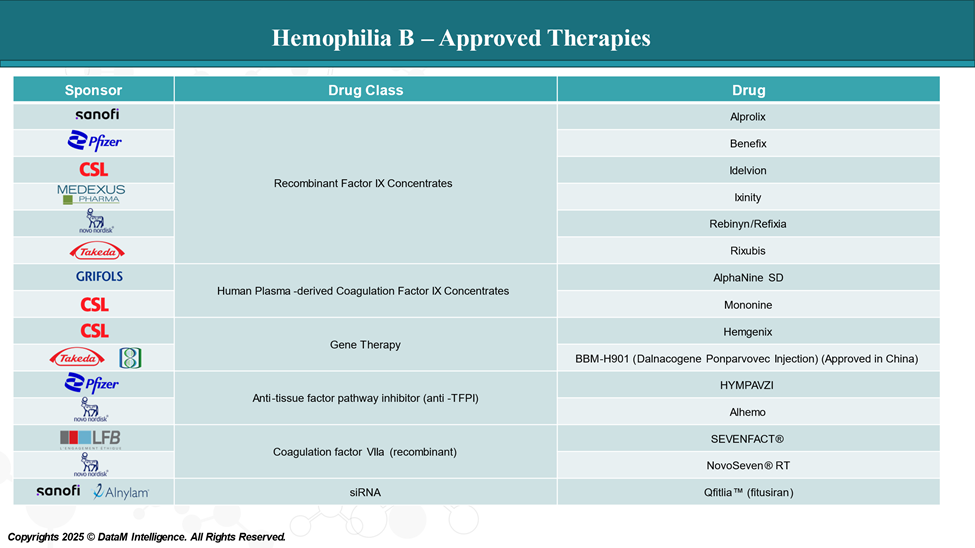
These engineered proteins have become the cornerstone of modern Hemophilia B therapy.
- Sanofi – Alprolix: A long-acting recombinant FIX Fc fusion protein, approved for both prophylaxis and treatment of bleeding episodes.
- Pfizer – BeneFIX: A widely used recombinant FIX product, known for its safety and efficacy in all age groups.
- CSL Behring – Idelvion: An albumin-fusion protein with one of the longest half-lives among FIX products, enabling infusions once every 1–2 weeks.
- Medexus Pharma – Ixinity: Offers consistent bleed protection and is indicated for both adults and children.
- Novo Nordisk – Rebinyn/Refixia: A glycoPEGylated recombinant FIX with an extended half-life, allowing for less frequent dosing.
- Takeda – Rixubis: A recombinant FIX concentrate specifically indicated for prophylaxis and perioperative management.
Human Plasma-Derived FIX
Though recombinant products are increasingly preferred, plasma-derived FIX concentrates remain in use, particularly in regions with limited access to advanced biologics.
- Grifols – AlphaNine SD: A solvent/detergent-treated plasma-derived FIX, ensuring viral safety.
- CSL Behring – Mononine: A highly purified plasma-derived FIX product used for routine prophylaxis and acute bleeding episodes.
Breakthrough Therapies: Gene Therapy & Beyond
Gene therapy represents a potential functional cure for Hemophilia B by introducing a working copy of the FIX gene into liver cells, allowing the body to produce its own FIX.
Approved and Late-Stage Gene Therapies
- CSL – Hemgenix: The first FDA- and EMA-approved gene therapy for Hemophilia B, delivering sustained FIX expression from a single intravenous infusion.
- Takeda/Belief BioMed – BBM-H901 (Dalnacogene Ponparvovec): An investigational gene therapy currently in development, promising strong and durable FIX expression levels.
- BIOCAD – ANB-002: Recombinant AAV-based gene therapy, currently in Phase III.
Gene Editing & Novel Genetic Platforms
- Regeneron – REGV131-LNP1265: In vivo CRISPR/Cas9-based Factor IX gene insertion (Phase II).
- Be Biopharma – BE-101: Pioneering B cell-based gene therapy (Phase I/II), aiming for durable FIX production via modified B lymphocytes.
Innovative Non-Factor Therapies: Redefining Hemostasis
Anti-TFPI Therapies
These agents block the tissue factor pathway inhibitor to rebalance coagulation.
- Pfizer – HYMPAVZI: A new entrant targeting the TFPI pathway to rebalance hemostasis.
- Novo Nordisk – Alhemo: Another anti-TFPI agent showing promise in reducing bleeding frequency.
- Suzhou Alphamab – KN057: Monoclonal antibody (mAb), Phase III.
siRNA Therapeutics
- Sanofi/Alnylam – Qfitlia™ (Fitusiran): A small interfering RNA (siRNA) drug designed to silence antithrombin expression, enhancing thrombin generation and promoting clot formation even in the absence of sufficient FIX.
Other Novel Agents in Development
- Staidson (Beijing) – Bemiltenase alfa (STSP-0601): A Factor X-activating enzyme, in Phase III.
- Equilibra Bioscience – SR604: Anti-activated protein C (APC) mAb (Phase I), targeting a different anticoagulant mechanism.
- Jiangsu Gensciences – SS109: Recombinant human Factor VII-Fc (rhFVII-Fc) fusion protein (Phase II).
- TiumBio – TU7710: Recombinant Factor VIIa (rFVIIa), Phase I.
Recombinant Factor VIIa (rFVIIa) – Approved Products
- LFB – SEVENFACT®: A recombinant activated FVII therapy for treating bleeding episodes, especially in patients with inhibitors.
- Novo Nordisk – NovoSeven® RT: A fast-acting FVIIa product, widely used for managing breakthrough bleeds
Conclusion: Toward a Personalized, Curative Future
The Hemophilia B treatment landscape in 2025 offers more choices than ever before from traditional plasma-derived products and recombinant FIX concentrates to groundbreaking gene therapy and siRNA-based innovations. These options allow for more personalized care plans tailored to each patient's lifestyle, bleeding profile, and treatment goals.
From weekly FIX infusions to one-time gene therapy and targeted gene editing, Hemophilia B management is undergoing a paradigm shift. The integration of gene-based approaches, novel biologics, and rebalancing agents will likely allow for individualized treatment strategies, minimizing bleeding risk while enhancing quality of life.
As science continues to advance, Hemophilia B is transitioning from a chronic condition managed with frequent infusions to one that may be treated and potentially cured with a single dose.
With a robust pipeline spanning advanced recombinant proteins, RNA interference, monoclonal antibodies, and CRISPR-based editing, Hemophilia B is no longer a static condition it is a field of rapid innovation, with the ultimate goal of long-term remission or even a cure.