Disease Overview:
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a chronic autoimmune disease characterized by inflammation, fibrosis, and damage to blood vessels. This condition can lead to thickening and hardening of the skin, as well as involvement of internal organs such as the lungs, gastrointestinal system, heart, and kidneys.
SSc is typically classified into two major subtypes based on the extent and location of skin involvement:
- Diffuse cutaneous systemic sclerosis (dcSSc)
- Limited cutaneous systemic sclerosis (lcSSc)
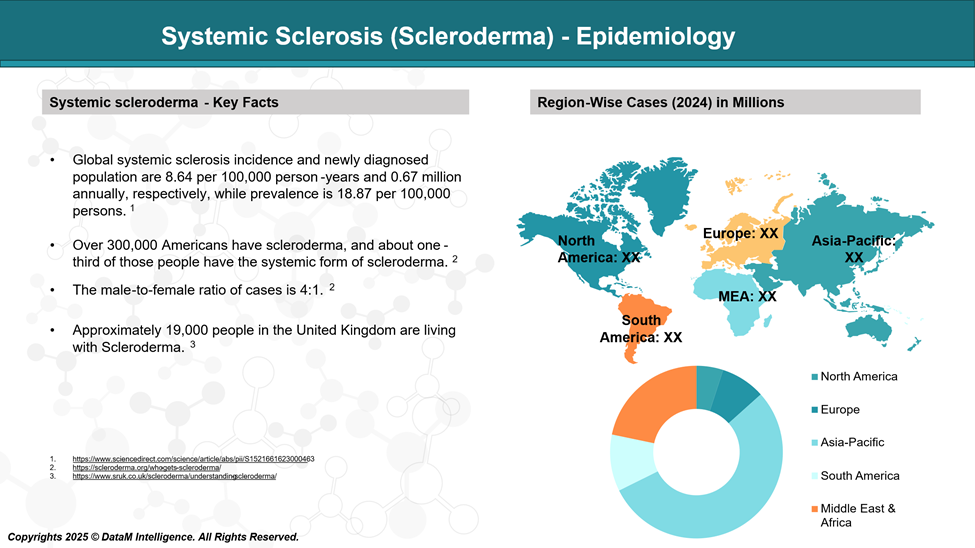
Epidemiology Analysis (Current & Forecast)
Approved Drugs - Sales & Forecast
Currently, there are no FDA-approved treatments that directly cure scleroderma (systemic sclerosis) or halt its progression completely. However, the FDA has approved several drugs to manage specific symptoms and complications associated with the disease. These include medications for lung involvement, skin fibrosis, and vascular issues.
Pain Management: Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), such as ibuprofen, naproxen, diclofenac, and celecoxib, are often used to ease pain and reduce inflammation.
Immune Suppressants: Drugs like methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, and cyclophosphamide work by dampening the immune system’s activity to help control the autoimmune process driving the disease.
Biologic Therapies: Administered through intravenous infusion, biologics like tocilizumab (Actemra) may be prescribed, particularly in cases involving lung complications related to scleroderma.
Nintedanib (Ofev): Approved for Interstitial lung disease (ILD) associated with systemic sclerosis.
Medications for Heart and Kidney Health: To manage scleroderma-related high blood pressure, medications such as sildenafil, tadalafil, and ambrisentan may be used. In some cases, captopril is given to help address kidney issues associated with the disease.
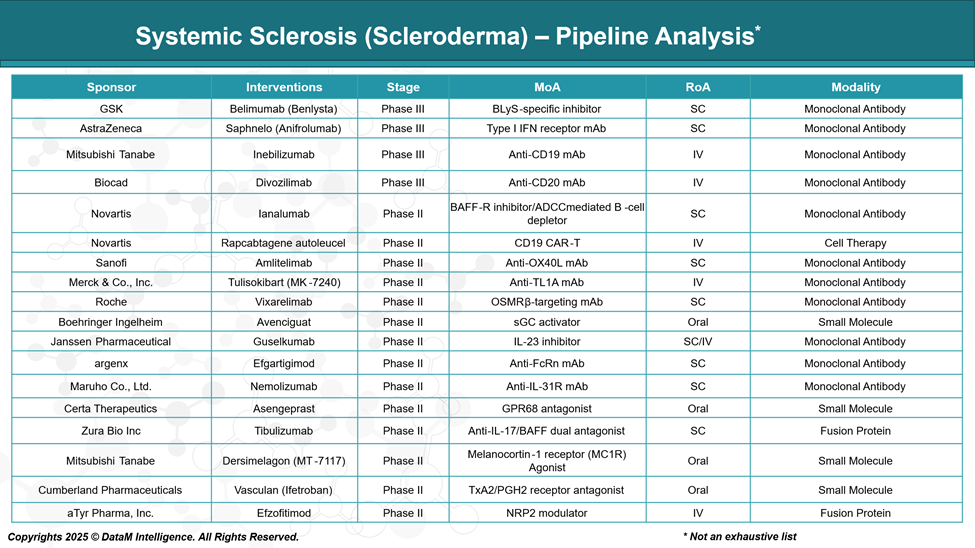
Pipeline Analysis and Expected Approval Timelines
As of 2025, the therapeutic pipeline for systemic sclerosis (SSc) is expanding, with various stages of development, including small molecules, biologics, cell therapies, and gene-based treatments. These emerging therapies aim to address the complex pathophysiology of SSc, targeting fibrosis, immune dysregulation, and vascular abnormalities.
Competitive Landscape and Market Positioning
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) remains a significant unmet medical need, with no FDA-approved disease-modifying therapy currently available. As a result, the competitive landscape is both dynamic and opportunistic, with numerous pharmaceutical companies racing to bring the first approved treatment to market. The pipeline is rich with advanced-stage candidates targeting immune dysregulation, fibrosis, and vascular dysfunction, which are the core pathological features of SSc.
Company | Drug Name | Target / MOA | Key Differentiator / Strategic Positioning | Potential Clinical Focus in SSc | Competitive Note |
GSK | Belimumab (Benlysta) | BLyS-specific inhibitor | First B-cell targeting biologic with a lupus track record | Autoimmune modulation | High brand recognition; fast track for B-cell driven SSc subsets |
AstraZeneca | Anifrolumab (Saphnelo) | Type I IFN receptor mAb | Strong lupus data; inhibits type I IFN signaling | Inflammatory and fibrotic components | Positioned to compete in skin and lung-dominant SSc |
Mitsubishi Tanabe | Inebilizumab | Anti-CD19 mAb | Broader B-cell targeting vs. CD20; long-acting | Immune-mediated tissue damage | Broader depletion may offer higher efficacy; needs safety differentiation |
Biocad | Divozilimab | Anti-CD20 mAb | Traditional B-cell depletion approach | Fibrotic and vasculopathic SSc | Competes directly with rituximab-class therapies |
Novartis | Ianalumab | BAFF-R inhibitor / ADCC B-cell depletion | Dual mechanism: inhibits survival + induces depletion | Immune-driven SSc with B-cell signature | Innovative dual-action approach; may be ideal for early SSc |
Novartis | Rapcabtagene autoleucel | CD19 CAR-T | Personalized, deep immunomodulation; high remission potential | Refractory or aggressive disease | High-cost, high-impact niche; logistical challenge in rare disease |
Sanofi | Amlitelimab | Anti-OX40L mAb | Immune tolerance restoration; T-cell focused | Early immune dysregulation | Could shift focus from fibrosis to immune reset strategy |
Merck & Co. | Tulisokibart (MK-7240) | Anti-TL1A mAb | Targets key Th1/Th17 cytokine axis | Skin and GI tract involvement | Broad application potential beyond SSc; inflammation-modifying niche |
Roche | Vixarelimab | OSMRβ-targeting mAb | Dual benefit: anti-fibrotic + anti-pruritic | Skin fibrosis and itching | Unique QoL-focused approach; could gain traction for dermatologic symptoms |
Boehringer Ingelheim | Avenciguat | sGC activator | Oral therapy; targets vascular dysfunction | Raynaud’s, PAH, digital ulcers | First-in-class oral for vascular complications; high adherence potential |
Janssen Pharma | Guselkumab | IL-23 inhibitor | Modulates innate/adaptive pathways; repurposed from psoriasis | Cutaneous inflammation | Repurposing advantage: strong safety database |
argenx | Efgartigimod | Anti-FcRn mAb | Reduces pathogenic IgG levels; autoantibody-focused | Autoantibody-positive SSc subsets | Precision medicine profile: synergistic with other immunotherapies |
Maruho | Nemolizumab | Anti-IL-31R mAb | Focused on chronic itch and skin modulation | Pruritus, skin thickening | QoL enhancer could be a valuable add-on therapy |
Market Dynamics and Strategic Insights
- First-to-Market Race: GSK, AstraZeneca, Mitsubishi Tanabe, and Biocad are all in Phase III, making them top contenders for regulatory filings within the next 1–2 years.
- Differentiation Strategy: Companies like Novartis and Sanofi are focusing on unique mechanisms (e.g., BAFF-R inhibition, OX40L blockade) to create competitive edges in crowded autoimmune markets.
- Biologic Dominance: The majority of agents are monoclonal antibodies delivered via SC or IV routes, but oral agents like Avenciguat are emerging with more convenient dosing profiles.
- Precision Immunotherapy: CAR-T (Novartis) and FcRn inhibition (argenx) represent the push toward highly tailored, mechanism-specific interventions in autoimmune diseases.
Key Companies:

Target Opportunity Profile (TOP)
Here is a Target Opportunity Profile for systemic sclerosis (SSc), outlining the key attributes that emerging therapies must demonstrate to gain a competitive foothold and ultimately achieve regulatory and commercial success. This profile is based on current gaps in treatment, clinical trends, and payer/regulatory expectations:
Target Opportunity Profile for Emerging SSc Therapies
Attribute | Ideal Profile | Rationale / Market Need |
Efficacy | - Demonstrated organ-specific benefit (skin, lung, kidney, vascular) | High unmet need for therapies that provide meaningful, measurable clinical benefit in target organ systems |
Safety | - Acceptable long-term safety profile | Chronic autoimmune disease requires sustained treatment, so safety is critical to avoid long-term harm |
Mechanism of Action (MoA) | - Novel or well-validated immunologic or antifibrotic target | Therapies must differentiate themselves via precision targeting or multi-pathway modulation |
Route of Administration (RoA) | - Preferably subcutaneous (SC) or oral | Patient adherence and quality of life are enhanced by convenient dosing |
Dosing Regimen | - Low frequency (monthly or less) | Simplified regimens reduce treatment burden, support outpatient use, and improve adherence |
Modality | - Biologic or small molecule with validated delivery platform | Modalities must align with SSc heterogeneity—e.g., biologics for immune SSc, cell therapy for refractory |
Organ-Specific Impact | - Strong benefit in interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD), skin fibrosis, or vascular complications | These are the leading causes of morbidity and mortality in SSc, especially ILD and PAH |
Onset of Action | - Demonstrated effect within 12–16 weeks | Faster responses improve clinical decision-making and reduce risk of irreversible damage |
Durability of Effect | - Sustained benefit over 12+ months | Long-term benefit is crucial for chronic disease control |
Combination Potential | - Compatible with existing standards of care (e.g., MMF, CCBs, PDE5 inhibitors) | Many patients are on polypharmacy; new drugs must be co-therapy friendly |
Innovation / Differentiation | - First-in-class or best-in-class potential | Stand out in a crowded pipeline with novel target, superior delivery, or holistic mechanism |
Biomarker Correlation | - Linked to mechanistic biomarkers (e.g., BAFF levels, IFN signature, skin biopsy) | Biomarker-driven strategies improve trial design and personalized treatment pathways |
Regulatory Strategy | - Orphan drug designation | Aligning with regulatory incentives accelerates development and market entry |
Strategic Summary
To succeed in systemic sclerosis, emerging therapies must:
- Balance efficacy with tolerability, given the systemic and long-term nature of the disease.
- Demonstrate clear organ-specific benefits—particularly in lung fibrosis and vascular complications, which drive mortality.
- Offer a convenient, low-burden treatment (SC or oral preferred) that fits into real-world practice.
- Innovate either in MoA, delivery, or clinical differentiation (QoL, skin relief, biomarker stratification).
- Be designed for combination use in multi-mechanistic regimens without compounding safety risks.
Why Buy Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report?
Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report is designed to give you a strategic advantage by providing deep insights into the pharmaceutical landscape. Here’s how it benefits you and your business: