Disease Overview:
Stargardt disease is a rare inherited eye disorder caused by the buildup of fatty substances in the macula, the central part of the retina responsible for sharp vision. This condition stems from mutations in the ABCA4 gene located on chromosome 1, which codes for a protein involved in transporting molecules within the retina.
These genetic changes lead to the accumulation of byproducts from the visual cycle in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), ultimately causing damage to photoreceptor cells and resulting in progressive vision loss.
Epidemiology Analysis (Current & Forecast)
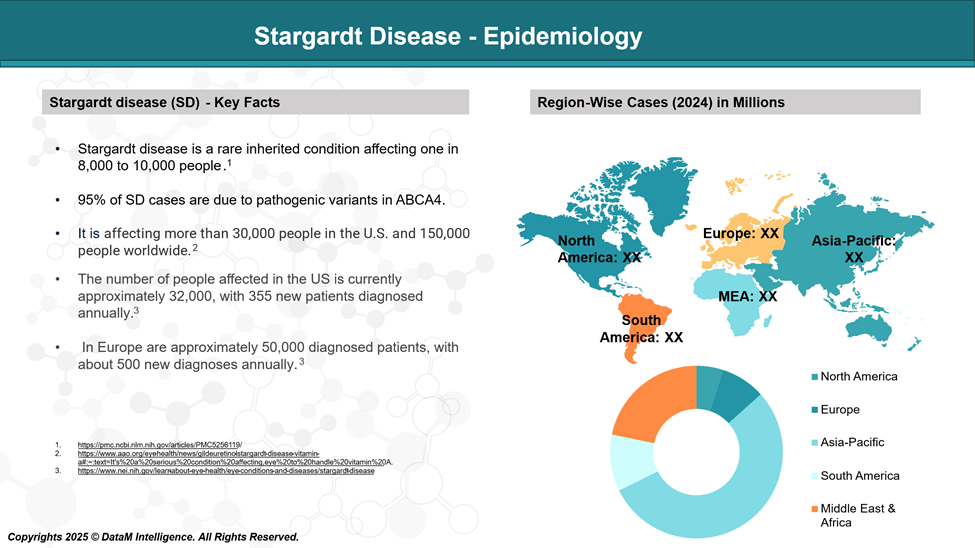
Stargardt disease is the most common inherited macular dystrophy in both adults and children, with a global prevalence of 1 in 8000–10,000.
Approved Drugs - Sales & Forecast
Stargardt disease currently has no definitive cure, and treatment is primarily aimed at managing symptoms and slowing the progression of vision loss.
In rare instances, patients may develop neovascularization, a condition in which abnormal blood vessels grow beneath the retina and leak fluid or blood. This can cause a sudden decline in central vision. When this occurs, ophthalmologists often administer anti-VEGF medications through injections into the eye to limit the growth of these vessels and stabilize vision.
Preventive care is also essential. Patients are typically encouraged to minimize exposure to bright light by using UV-protective sunglasses and to avoid smoking, both of which may contribute to retinal damage.
Pipeline Analysis and Expected Approval Timelines
Researchers are actively investigating new therapies, including gene-based treatments and small molecules, which may offer more effective solutions in the future.
Competitive Landscape and Market Positioning
Stargardt disease, a form of inherited macular degeneration, currently has no approved therapies, creating a significant unmet medical need. This has led to a competitive pipeline of clinical-stage programs targeting various aspects of the disease's pathophysiology. Given the absence of approved treatments, the competitive landscape is defined not by market share but by clinical progress, innovation, and differentiation in mechanism of action (MoA). Companies are strategically positioning their candidates to capture first-mover advantage and establish benchmarks in efficacy, safety, and durability.
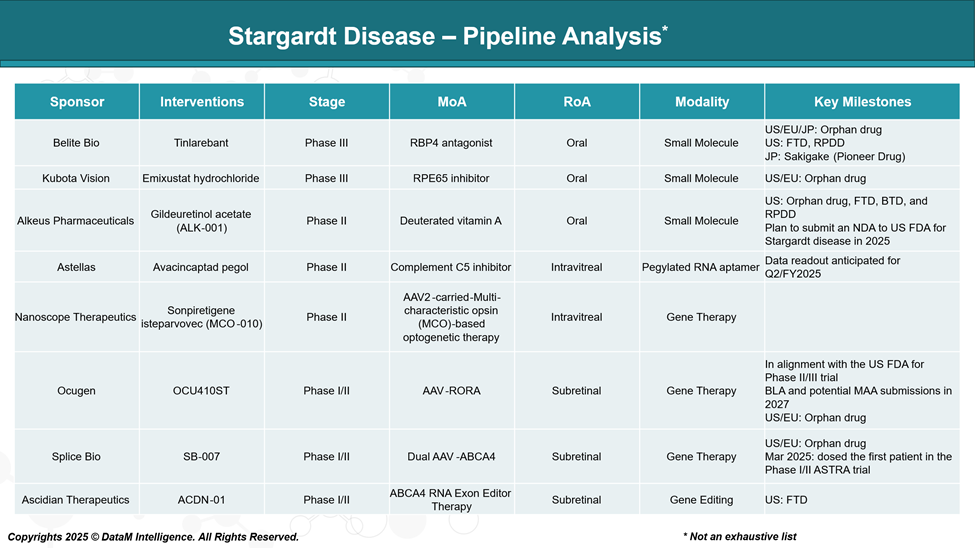
Sponsor | Asset | MoA | Delivery Method | Therapeutic Modality | Target Segment | Key Differentiators / Insights |
Belite Bio | Tinlarebant | RBP4 antagonist (reduces toxic retinoid accumulation) | Oral | Small molecule | Broad Stargardt population, early-stage | First-to-market potential; oral, non-invasive; upstream intervention on vitamin A transport |
Kubota Vision | Emixustat | RPE65 inhibitor (modulates visual cycle) | Oral | Small molecule | Early- to mid-stage patients | Competes directly with Tinlarebant; visual cycle modulator; prior AMD experience informs Stargardt strategy |
Alkeus Pharmaceuticals | ALK-001 (Gildeuretinol acetate) | Deuterated Vitamin A (prevents toxic dimer formation) | Oral | Modified vitamin A analog | Early intervention; younger patients | Long-term disease prevention focus; unique chemical stability through deuteration |
Astellas | Avacincaptad pegol | Complement C5 inhibitor (anti-inflammatory) | Intravitreal | Antibody fragment (RNA aptamer) | Patients with active degeneration or inflammation | Leveraging complementary biology from AMD, cross-indication potential |
Nanoscope Therapeutics | MCO-010 | AAV2-delivered MCO optogenetics (restores light sensitivity) | Intravitreal | Gene therapy/ optogenetics | Late-stage, advanced vision loss | Mutation-independent; vision restoration potential even in non-functional photoreceptors |
Ocugen | OCU410ST | AAV-RORA (gene modulator of retinal survival pathways) | Subretinal | Gene therapy | Early- to mid-stage; inflammation & degeneration modulation | Unique transcription factor target; inflammation-focused gene modulation |
Splice Bio | SB-007 | Dual AAV-based ABCA4 gene augmentation | Subretinal | Gene therapy | Genetically confirmed ABCA4 mutation patients | Dual-vector platform enables delivery of large ABCA4 gene; mutation-specific therapy |
Ascidian Therapeutics | ACDN-01 | RNA exon editor for ABCA4 | Non-viral (delivery under evaluation) | RNA editing therapy | Genetically confirmed ABCA4 mutation patients | Novel non-viral exon-editing platform; potential for repeat dosing and high precision |
Market Positioning:
- Belite Bio and Kubota Vision are strongest on timing and convenience.
- Nanoscope and Ascidian may dominate long-term if advanced technologies demonstrate robust, mutation-independent efficacy.
- Alkeus is uniquely preventative likely to complement rather than compete with vision restoration approaches.
Key Companies:

Target Opportunity Profile (TOP)
For Stargardt Disease, emerging therapies must demonstrate a compelling Target Opportunity Profile (TOP) to gain regulatory approval, attract payer support, and meet patient needs. Given the current lack of approved treatments, the bar is both high in terms of unmet need and complex due to the biology of the disease.
Target Opportunity Profile – Stargardt Disease
Category | Ideal Criteria for Market Entry |
Safety | - No ocular toxicity (e.g., inflammation, retinal detachment) |
Efficacy | - Slows or halts the progression of retinal degeneration |
Mechanism of Action (MoA) | - Direct correction or replacement of ABCA4 function |
Route of Administration (RoA) | - Preferably intravitreal (less invasive) |
Innovation | - Novel delivery platforms (dual AAV, lentivirus, LNPs) for large genes |
Modality | - Gene therapy (dual AAV, lentiviral) |
Why Buy Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report?
Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report is designed to give you a strategic advantage by providing deep insights into the pharmaceutical landscape. Here’s how it benefits you and your business: