Disease Overview:
Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a common sleep disorder that disrupts normal breathing patterns during sleep. Individuals with OSA experience repeated episodes where airflow to the lungs is reduced or completely blocked. This interruption is typically due to the relaxation and collapse of soft tissues in the upper airway, including the throat and tongue, obstructing the air passage.
Epidemiology Analysis (Current & Forecast)
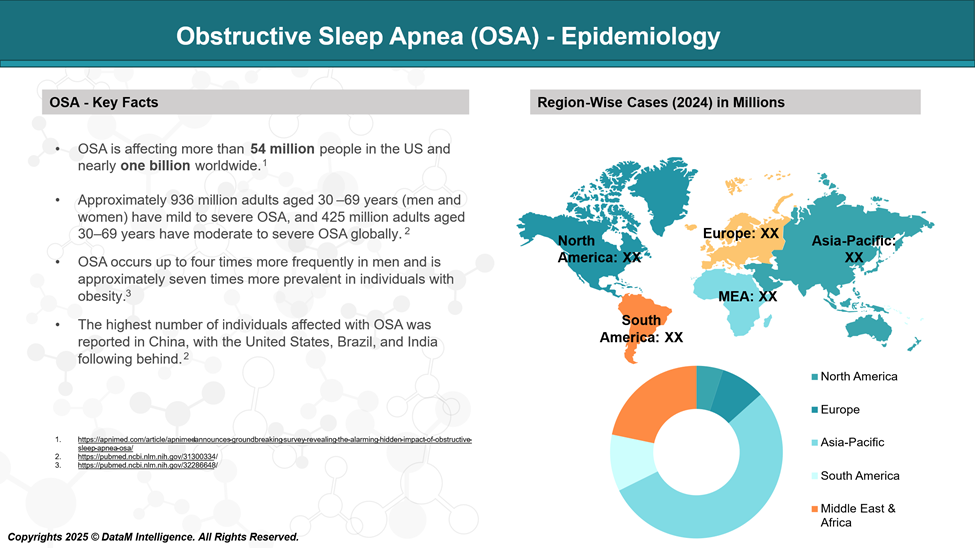
It is estimated that OSA affects 936 million adults worldwide, with 425 million suffering from moderate to severe OSA.
Approved Drugs - Sales & Forecast
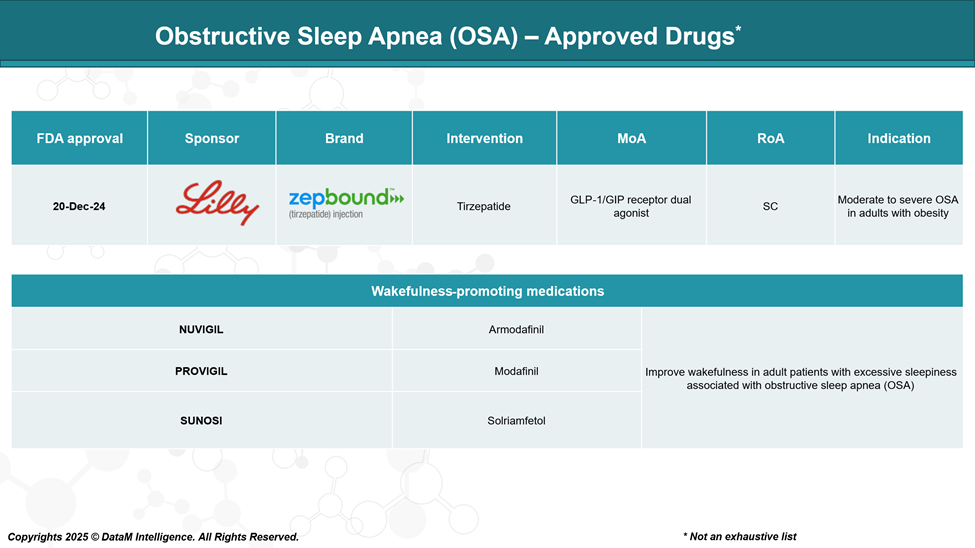
The U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approved Zepbound (tirzepatide) as the first drug specifically indicated for the treatment of moderate to severe OSA in adults with obesity.
While Zepbound is the only FDA-approved drug specifically for OSA, other medications are utilized to manage associated symptoms, particularly excessive daytime sleepiness: Modafinil (Provigil) and Armodafinil (Nuvigil). A dopamine and norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor, solriamfetol (Sunosi) is also approved to improve wakefulness in adults with OSA-related excessive daytime sleepiness.
Pipeline Analysis and Expected Approval Timelines
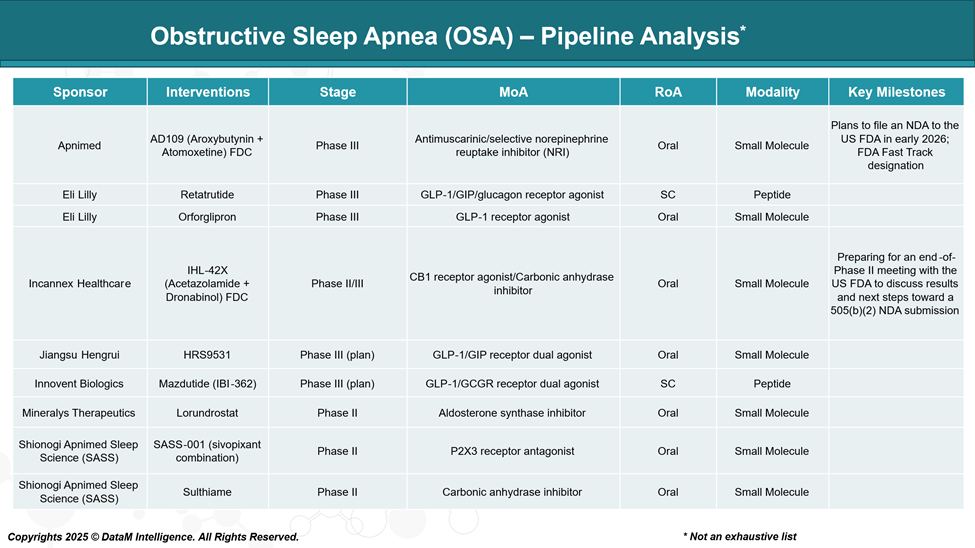
The development of pharmacological medications for obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is progressing rapidly, with a diverse pipeline of therapies targeting various mechanisms. This expansion aims to provide alternatives or adjuncts to traditional treatments like continuous positive airway pressure (CPAP) therapy.
Competitive Landscape and Market Positioning
The competitive landscape for OSA is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by the emergence of novel pharmacological therapies alongside traditional device-based treatments.
Key industry players are now investing heavily in both symptom management and disease-modifying treatments, with a strategic focus on oral, fixed-dose combinations and metabolic agents. .
OSA Competitive Landscape & Market Positioning
Company | Drug | Stage | Target | Unique Selling Point |
Eli Lilly | Zepbound | Approved | Obese OSA | First approved drug; metabolic benefits |
Eli Lilly | Retatrutide | Phase III | Obese OSA | Triple agonist; stronger metabolic action |
Eli Lilly | Orforglipron | Phase III | Obese OSA | Oral GLP-1; user convenience |
Apnimed | AD109 | Phase III | Non-obese, mild/moderate OSA | Non-weight-based mechanism; nightly pill |
Apotex/Neuraxpharm | NUVIGIL / PROVIGIL | Approved | Symptom relief | Wakefulness agents; adjunct to CPAP |
Axsome | SUNOSI | Approved | Symptom relief | Dual-action stimulant |
Incannex | IHL-42X | Phase II/III | General OSA | Multimodal, cannabinoid-enhanced FDC |
Key Companies:

Target Opportunity Profile (TOP)
To outperform currently approved treatments for OSA, including device-based therapy (e.g., CPAP) and pharmacotherapies like Zepbound (tirzepatide), SUNOSI, and PROVIGIL—emerging drugs must address clear gaps in safety, efficacy, mechanism of action, route of administration, and dosing convenience.
Below is a Target Opportunity Profile outlining what next-generation therapies need to deliver to become competitive or best-in-class:
Target Opportunity Profile – Emerging Therapies for OSA
Category | Target Profile | Strategic Rationale |
Safety Profile | - No significant cardiovascular (e.g., blood pressure, arrhythmia) or neuropsychiatric adverse effects | - Current therapies like modafinil and solriamfetol are stimulants with cardiovascular risks |
Efficacy Benchmarks | - ≥50% reduction in AHI in at least 50% of treated patients | - Efficacy must rival CPAP and weight-loss agents, especially for moderate-to-severe OSA |
Mechanism of Action | - Targets airway patency (e.g., upper airway muscle tone, arousal threshold, ventilatory drive) | - Metabolic agents are not suitable for all patients; non-weight-based drugs can address lean OSA patients |
Route of Administration | - Oral (tablet/capsule) is ideal for chronic nightly use | - Oral agents offer better compliance and scalability than injectables (e.g., Zepbound, GLP-1s) |
Dosing and Convenience | - Once-nightly dosing aligned with the sleep cycle | - Dosing simplicity increases market access and patient preference |
Patient Segmentation | - Effective in CPAP-intolerant patients | - CPAP non-adherence remains a major treatment gap |
Regulatory Advantage | - Clearly defined clinical endpoints (AHI, ESS, ODI) | - Regulators are increasingly open to novel endpoints (e.g., ESS and patient-reported outcomes) |
Why Buy Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report?
Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report is designed to give you a strategic advantage by providing deep insights into the pharmaceutical landscape. Here’s how it benefits you and your business: