Disease Overview:
IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD) is a rare, chronic autoimmune condition characterized by inflammation and fibrosis in one or more organs. It is associated with high levels of IgG4-positive plasma cells in affected tissues and, often, elevated levels of IgG4 in the blood.
The disease can affect various organs such as the pancreas, salivary glands, kidneys, lungs, and lymph nodes, often causing swelling or mass-like lesions that can mimic cancer or infections. IgG4-RD typically responds well to steroid treatment but may relapse or require long-term immunosuppressive therapy.
IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD) is characterized by:
Tumefactive lesions (mass-like enlargements of affected organs)
Dense lymphoplasmacytic infiltrates rich in IgG4-positive plasma cells
Storiform fibrosis (a whorled pattern of fibrous tissue)
Elevated serum IgG4 levels (in many but not all patients)
Key Features:
Multisystem involvement: Can affect nearly any organ, including:
Pancreas (Autoimmune pancreatitis type 1)
Biliary tract
Salivary and lacrimal glands
Kidneys, lungs, retroperitoneum, aorta, thyroid, and more.
Often mimics malignancy, infection, or other autoimmune conditions, making diagnosis challenging.
Response to corticosteroids is typically good, which is a hallmark of the disease.
Pathophysiology:
The exact cause is unclear, but it involves dysregulated immune responses, including T-helper 2 (Th2) and regulatory T cell activity, with production of cytokines like IL-4 and IL-10 that promote IgG4 production.
Fibrosis and organ dysfunction result from chronic inflammation and immune-mediated damage.
Diagnosis:
Based on a combination of:
Clinical findings
Serology (elevated IgG4 levels)
Imaging
Histopathology (showing hallmark features mentioned above)
Treatment:
First-line: Glucocorticoids (e.g., prednisone)
Steroid-sparing agents: Rituximab (anti-CD20), azathioprine, mycophenolate mofetil in refractory or relapsing cases
Prognosis:
Generally favorable with treatment, but relapses are common, and long-term organ damage can occur if not properly managed.
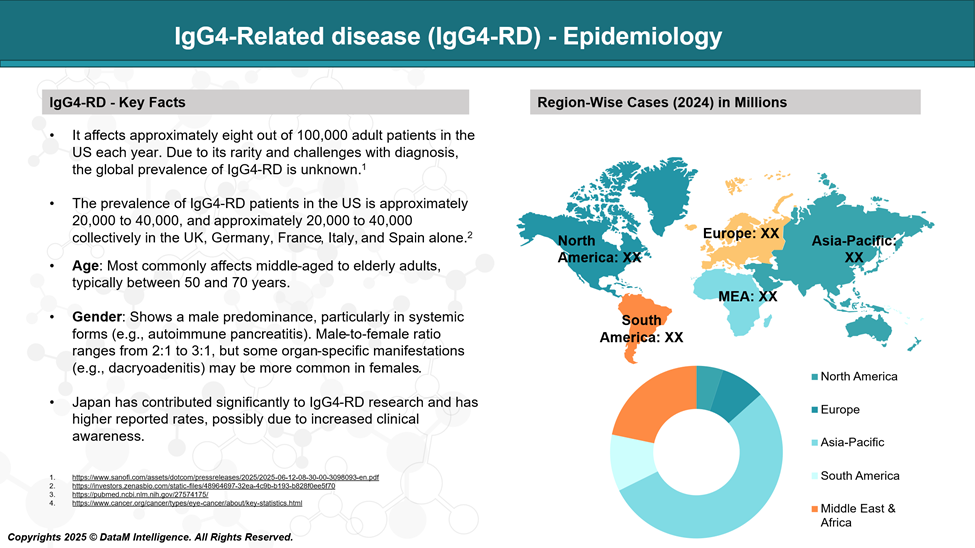
Epidemiology Analysis (Current & Forecast)
IgG4-RD is considered a rare disease, and its true incidence and prevalence are still being defined due to under-recognition and diagnostic challenges. However, available epidemiological data suggest the following:
Global Estimates:
Prevalence: Estimated at 2.5 to 10 cases per 100,000 population, but this varies by region and diagnostic criteria.
Incidence: Around 0.28 to 1.08 per 100,000 persons per year in population-based studies.
Organ Involvement Frequencies (approximate):
Pancreas (Type 1 Autoimmune Pancreatitis): Most common form.
Salivary/Lacrimal Glands (Mikulicz’s disease): ~25–50%
Kidneys (IgG4-related tubulointerstitial nephritis): ~15%
Retroperitoneum (retroperitoneal fibrosis): ~10–15%
Lymphadenopathy and lung involvement: ~10–20%
Approved Drugs - Sales & Forecast
Uplizna® (inebilizumab-cdon) is the First and Only FDA-Approved Drug for IgG4-Related Disease
Overview
Brand Name: Uplizna®
Generic Name: Inebilizumab-cdon
Developer: Horizon Therapeutics (an Amgen company)
FDA Approval Date: April 7, 2025
Indication: Treatment of adults with IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD)
Approval Status: First and only FDA-approved therapy specifically for IgG4-RD
Mechanism of Action
Inebilizumab is a humanized monoclonal antibody that targets CD19, a surface protein found on a broad range of B cells, including:
Naïve B cells
Memory B cells
Plasmablasts and some plasma cells (which are often missed by anti-CD20 therapies like rituximab)
By depleting these CD19+ B cells, Uplizna helps to:
Reduce production of IgG4-positive plasma cells
Suppress chronic inflammation and fibrosis, which are hallmark features of IgG4-RD
Offer broad and durable B-cell suppression
Clinical Trial Evidence: The MITIGATE Trial
Name: MITIGATE (NCT04540497)
Type: Phase III, randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled
Population: 135 patients with active IgG4-RD
Endpoints:
Primary: Time to first disease flare
Secondary: Annualized flare rate, steroid-sparing potential, quality of life improvements
Pipeline Analysis and Expected Approval Timelines
Following the recent FDA approval of Uplizna® (inebilizumab) in April 2025, there is growing momentum in the development of targeted therapies for IgG4-RD. Below is an overview of notable pipeline therapies, their mechanisms, clinical stage, and anticipated timelines.
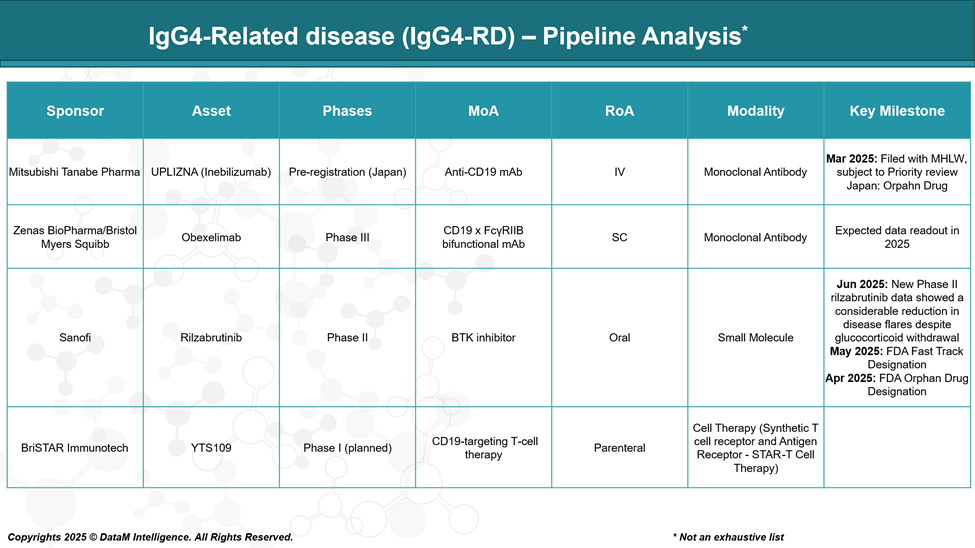
Inebilizumab (UPLIZNA®) – Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma (Japan)
Mechanism: Anti-CD19 monoclonal antibody
Modality: IV monoclonal antibody
Development Status: FDA-approved in the U.S. (April 2025)
Pre-registration in Japan by Mitsubishi Tanabe
Highlights:
Depletes CD19⁺ B cells, including plasmablasts and short-lived plasma cells, addressing the core pathogenic drivers of IgG4-RD.
Approved based on the MITIGATE trial, which showed a 77% reduction in flare risk.
Japan launch expected 2025–26.
Strategic Potential:
Establishes global franchise for UPLIZNA beyond U.S.
Competes with off-label rituximab in markets without UPLIZNA access.
Obexelimab (Zenas BioPharma / Bristol Myers Squibb)
Mechanism: CD19 x FcγRIIB bispecific monoclonal antibody
Modality: Fc-engineered monoclonal antibody
Development Status: Phase III (2024–2026)
Highlights:
Uniquely inhibits B-cell activity via FcγRIIB co-engagement without full depletion.
Previously known as XmAb5871, licensed from Xencor to Zenas.
Demonstrated clinical benefit in Phase 2, reducing disease activity and IgG4 levels.
Strategic Potential:
Safer profile compared to full B-cell depletion (less infection risk).
Potentially suitable for maintenance therapy or patients intolerant to immunosuppressants.
Positioned as a next-generation immunomodulator.
Rilzabrutinib – Sanofi
Mechanism: BTK (Bruton’s Tyrosine Kinase) inhibitor
Modality: Oral small molecule
Development Status: Phase II (2024–2025)
Highlights:
BTK is essential in B-cell receptor signaling; inhibition suppresses B-cell activation without depleting cells.
Oral route offers superior convenience and potential steroid-sparing benefits.
Already under development for pemphigus vulgaris and other autoimmune conditions.
Strategic Potential:
First oral targeted therapy for IgG4-RD (if successful).
Could be differentiated by route of administration and flexibility in chronic use.
Potential for broad immunomodulatory benefit beyond B cells (BTK is also expressed in myeloid cells).
YTS109 – BriSTAR Immunotech
Mechanism: CD19-targeting T-cell therapy (likely a form of CAR-T or TCR-modified cells)
Modality: Engineered T-cell therapy
Development Status: Phase I (planned)
Highlights:
Represents a novel cell-based approach to deeply and selectively eliminate CD19⁺ B cells.
May offer long-term disease control with fewer doses due to a durable immune reset.
Preclinical success may translate to trials in high-risk, refractory IgG4-RD patients.
Strategic Potential:
First-in-class cell therapy in IgG4-RD if safety and efficacy hold.
May be reserved for severe, relapsing disease or used post-antibody failure.
Regulatory and manufacturing complexity is higher; long-term development pathway.
Competitive Landscape and Market Positioning
Market Overview & Current Standard
- IgG4-RD is a rare, chronic immune-mediated fibroinflammatory condition affecting multiple organs.
- Until 2025, treatment was largely off-label, relying on glucocorticoids and rituximab.
- The approval of Uplizna® (inebilizumab) by the FDA in April 2025 marked a paradigm shift:
- First targeted therapy approved specifically for IgG4-RD.
- Strong clinical trial data from MITIGATE showed a significant reduction in disease flares and steroid use.
Competitive Positioning Matrix
Drug | Company | MoA | Modality | Stage | Key Differentiator |
UPLIZNA | Horizon / Mitsubishi Tanabe | CD19 mAb | IV mAb | Approved (US); pre-reg (JP) | First-to-market, deep B-cell depletion |
Obexelimab | Zenas BioPharma / BMS | CD19 x FcγRIIB bifunctional mAb | IV mAb (engineered) | Phase III | B-cell inhibition without full depletion |
Rilzabrutinib | Sanofi | BTK inhibitor | Oral small molecule | Phase II | Oral delivery; non-depleting; immunomodulatory |
YTS109 | BriSTAR Immunotech | CD19-targeted T-cell therapy | Cell therapy | Phase I (planned) | Potential for long-lasting, deep remission |
Rituximab | (off-label) | CD20 mAb | IV mAb | Off-label | Legacy use; less effective vs plasmablasts |
Market Positioning Insights
UPLIZNA (Inebilizumab) – Market Leader
- Strengths:
- First-mover advantage
- High unmet need addressed with robust efficacy data (MITIGATE trial)
- Broad CD19 targeting—hits plasmablasts/plasma cells not covered by rituximab
- Weaknesses:
- IV administration only
- Potential infection risk due to broad B-cell depletion
- Positioning: Front-line targeted biologic for moderate-to-severe IgG4-RD
Obexelimab – Emerging Challenger
Strengths:
Selective B-cell inhibition via FcγRIIB without full depletion → possibly safer
Ideal for long-term maintenance or patients at higher infection risk
Weaknesses:
IV formulation, limited long-term safety data
Positioning: Second-line or alternative for patients needing immunomodulation without depletion
Rilzabrutinib – Disruptive Oral Option
Strengths:
Oral route = better compliance
Non-depleting mechanism = lower infection risk
Weaknesses:
Early-stage in IgG4-RD
May need a combination use in severe cases
Positioning: Oral, steroid-sparing agent for mild/moderate disease or maintenance therapy
Strategic Summary Table
Strategic Dimension | UPLIZNA | Obexelimab | Rilzabrutinib | YTS109 |
Approval Status | Approved | Phase III | Phase II | Preclinical |
MoA | CD19 depletion | CD19 inhibition | BTK inhibition | CD19 T-cell kill |
Dosing | IV, Q6M | IV | Oral | One-time (likely) |
B-cell Depletion | Yes | Partial | No | Yes (deep) |
Steroid-sparing? | Yes | Potential | Yes | Likely |
Best Fit Use | Moderate-severe | Maintenance | Mild-mod + combo | Refractory cases |
Key Risk | Infections | Durability | Efficacy | Safety/logistics |
Key Companies:

Target Opportunity Profile (TOP)
A Target Opportunity Profile (TOP) outlines the key attributes that emerging therapies must demonstrate to compete with or outperform current standards of care. In IgG4-Related Disease (IgG4-RD), the approval of UPLIZNA® has set a benchmark in efficacy and disease control.
New therapies must differentiate themselves on factors such as safety, convenience, mechanism, and innovation to capture a meaningful market share.
Parameter | Benchmark Set by UPLIZNA | Emerging Drug Opportunity |
Efficacy | 77% reduction in flares (MITIGATE trial) | Equal or superior flare prevention, remission induction, and effect in hard-to-treat subtypes |
Safety | Acceptable safety, but risk of infections due to broad B-cell depletion | Minimized infection risk; non-depleting or selective targeting preferred |
Mechanism of Action (MoA) | CD19 B-cell depletion (broad, including plasmablasts) | More selective or modulatory approach (e.g., FcγRIIB modulation, BTK inhibition, cell-specific depletion) |
Route of Administration (RoA) | Intravenous (every 6 months) | Oral or subcutaneous is preferred for chronic disease management |
Dosing Frequency | Twice yearly IV infusion | Less frequent (ideal) or oral daily (convenience); fewer healthcare touchpoints |
Modality | Monoclonal antibody | Oral small molecule, bispecific antibody, or cell therapy with differentiated value |
Durability of Response | Long-acting (B-cell depletion lasts months) | Comparable or longer remission periods; potential for disease modification |
Innovation/Novelty | First and only approved targeted therapy | Novel immune pathway modulation, targeted cell therapy, or functional cure potential |
Onset of Action | Moderate (weeks) | Faster onset (ideal); effective in flare settings or rapid taper from steroids |
Tolerability | Generally well-tolerated, but IV infusion burden | Improved tolerability profile (e.g., no infusion reactions, oral route, fewer AEs) |
Patient Segmentation | Broad eligibility (organ-involving disease) | Expandable to mild/moderate, steroid-dependent, or maintenance populations |
Strategic Implications
To outperform UPLIZNA or carve out competitive niches, emerging therapies should aim to:
- Surpass efficacy in subsets of patients with more severe or relapsing disease.
- Offer a safer profile, particularly for long-term use (e.g., avoid infections).
- Improve patient convenience with oral dosing or non-IV delivery.
- Enable precision or personalized treatment by offering MoA diversity.
- Provide value-based differentiation in pharmacoeconomics, compliance, and real-world outcomes.
Examples:
- Obexelimab targets CD19 without depleting B cells, potentially safer for long-term use.
- Rilzabrutinib offers an oral, non-depleting mechanism that could support early-line or maintenance therapy.
- YTS109 could define a new therapeutic category (cell therapy) if shown to offer deep, durable remission.
Conclusion: A Market in Transformation
- Uplizna dominates as the first FDA-approved option and sets the benchmark in efficacy.
- Pipeline players are aiming to fill specific gaps:
- Obexelimab: Less immunosuppression, safer long-term option.
- Rilzabrutinib: Oral route, steroid-sparing potential.
- YTS109: Future curative potential for relapsed/refractory disease.
- The market is moving from off-label immunosuppression to mechanism-based, stratified care.
Why Buy Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report?
Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report is designed to give you a strategic advantage by providing deep insights into the pharmaceutical landscape. Here’s how it benefits you and your business: