Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps - Disease Overview:
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (CRSwNP) is a long-lasting inflammatory condition of the nasal passages and sinuses, characterized by the growth of benign polyps. It leads to symptoms like nasal congestion, loss of smell, facial pressure, and nasal discharge. The condition is often linked to Type 2 inflammation and diseases like asthma or AERD. Diagnosis is confirmed through nasal endoscopy and imaging studies.
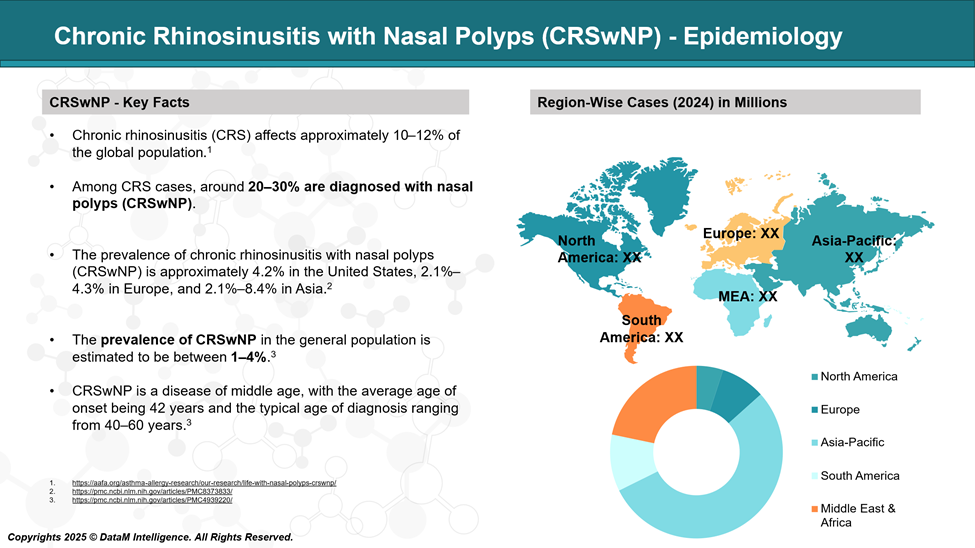
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps - Epidemiology Analysis (Current & Forecast)
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (CRSwNP) represents approximately 20–30% of all chronic rhinosinusitis (CRS) cases. It is more commonly observed in adults over 40 years of age, with a higher prevalence in males. Globally, CRSwNP affects an estimated 1–4% of the general population.
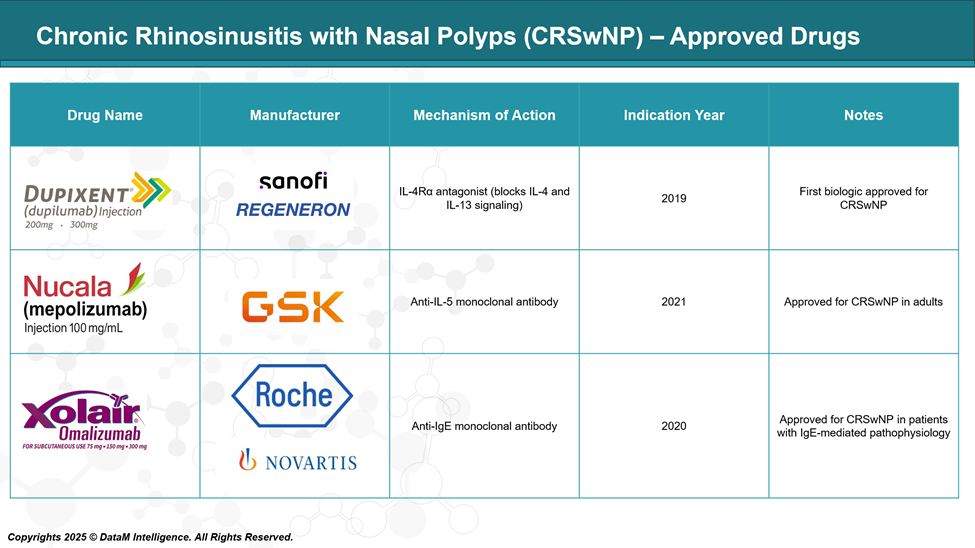
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps Approved Drugs - Sales & Forecast
The approval of biologics like Dupixent, Nucala, and Xolair has significantly shifted the treatment paradigm of CRSwNP, especially in patients with severe disease and Type 2 inflammation (eosinophilic, allergic). These agents have improved outcomes in patients unresponsive to steroids or those seeking alternatives to surgery.
Commonly Used Supportive/Adjunct Therapies
While not FDA-approved specifically for CRSwNP, the following treatments are commonly used off-label or as first-line management:
Treatment | Category | Examples | Role |
Intranasal corticosteroids | Anti-inflammatory | Fluticasone, Mometasone, Budesonide | First-line therapy for symptom control |
Oral corticosteroids | Systemic steroids | Prednisone | Used short-term for acute flare-ups |
Saline irrigation | Mechanical cleansing | Saline sprays or rinses | Helps reduce inflammation and clear mucus |
Antibiotics | For infection | Amoxicillin-clavulanate, doxycycline | Used if bacterial infection is suspected |
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps - Pipeline Analysis and Expected Approval Timelines
While biologics such as dupilumab, omalizumab, and mepolizumab have revolutionized treatment, they do not address all patient endotypes or deliver long-term remission in every case. As a result, the therapeutic pipeline is rapidly expanding with next-generation monoclonal antibodies and innovative biologics targeting upstream mediators such as TSLP, IL-33, and IL-4/IL-13 pathways.
This pipeline is marked by:
Upstream targets (e.g., TSLP, IL-33) aimed at broader immune modulation.
Bispecific antibodies (e.g., TSLP x IL-13) offering multi-pathway blockade.
Regional and biosimilar developments in Asian markets reflecting cost-driven innovation.
With more than a dozen agents in Phase II and III development, including tezepelumab, lebrikizumab, and depemokimab, the competitive landscape is poised to evolve rapidly. The ongoing focus is not only on efficacy but also on dosing convenience, endotype specificity, and cost-effectiveness, shaping the future standard of care for this chronic disease.
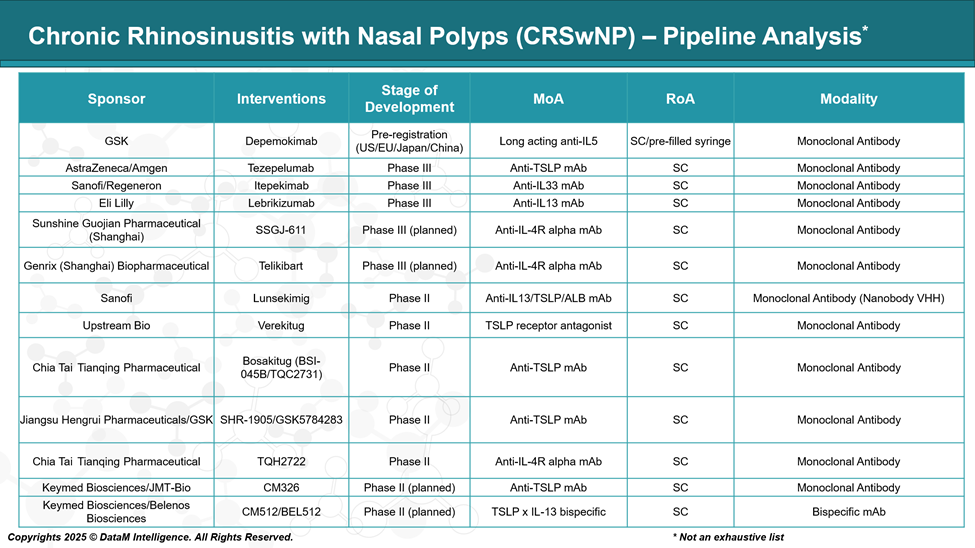
1. Depemokimab – GlaxoSmithKline
Stage: Pre-registration (US/EU/Japan/China)
MoA: Long-acting anti-IL-5 monoclonal antibody
Insight: Designed to reduce eosinophil activity with extended dosing intervals. It builds on GSK’s eosinophilic expertise (e.g., Nucala) and aims to offer improved patient convenience and disease control.
2. Tezepelumab – AstraZeneca / Amgen
Stage: Phase III
MoA: Anti-TSLP monoclonal antibody
Insight: Targets upstream in the Type 2 inflammation cascade. As TSLP is a key epithelial “alarmin,” Tezepelumab has potential for broader inflammatory suppression beyond eosinophils. Already approved for asthma; being explored for CRSwNP.
3. Itepekimab – Sanofi / Regeneron
Stage: Phase III
MoA: Anti-IL-33 monoclonal antibody
Insight: IL-33 is another alarmin involved in Type 2 inflammation. Blocking it may reduce multiple inflammatory mediators. Aims to position itself upstream like tezepelumab.
4. Lebrikizumab – Eli Lilly
Stage: Phase III
MoA: Anti-IL-13 monoclonal antibody
Insight: Targets IL-13 to reduce mucus production and epithelial inflammation. Already in development for atopic dermatitis; repurposed for CRSwNP.
5. SSGJ-611 – Sunshine Guojian Pharmaceutical
Stage: Phase III (planned)
MoA: Anti-IL-4R alpha monoclonal antibody
Insight: Blocks IL-4 and IL-13 pathways, mimicking the MoA of dupilumab. A potential biosimilar or competitor in Asian markets.
6. Telikibart – Genrix (Shanghai) Biopharmaceutical
Stage: Phase III (planned)
MoA: Anti-IL-4R alpha monoclonal antibody
Insight: Similar target as dupilumab. Aiming for an IL-4/IL-13 blockade alternative, especially in Chinese regulatory pathways.
7. Lunsekimig – Sanofi
Stage: Phase II
MoA: Anti-IL-13/TSLP/Albumin fusion monoclonal antibody
Insight: A novel multi-target fusion antibody, aiming for enhanced efficacy by targeting both TSLP and IL-13. Albumin fusion allows a longer half-life.
8. Verekitug – Upstream Bio Inc.
Stage: Phase II
MoA: TSLP receptor antagonist
Insight: Unlike antibodies that neutralize TSLP itself, this blocks the receptor. Potentially more efficient at dampening TSLP signaling in nasal mucosa.
9. Bosakitug (BSI-045B / TQC2731) – Chia Tai Tianqing
Stage: Phase II
MoA: Anti-TSLP monoclonal antibody
Insight: One of several emerging anti-TSLP antibodies in Asia, aiming to replicate or improve upon Tezepelumab’s upstream immunomodulation.
10. SHR-1905 / GSK5784283 – Jiangsu Hengrui / GSK
Stage: Phase II
MoA: Anti-TSLP monoclonal antibody
Insight: A collaboration between Chinese and global pharma. Reflects growing competition in the TSLP space, with potential for co-development across regions.
11. TQH2722 – Chia Tai Tianqing
Stage: Phase II
MoA: Anti-IL-4R alpha monoclonal antibody
Insight: Likely targeting a similar niche as dupilumab, with an aim for regional pricing and access advantages.
12. CM326 – Keymed Biosciences / JMT-Bio
Stage: Phase II (planned)
MoA: Anti-TSLP monoclonal antibody
Insight: Represents another player entering the TSLP race; likely focusing on Asia-Pacific trials first.
13. CM512 / BEL512 – Keymed Biosciences / Belenos Biosciences
Stage: Phase II (planned)
MoA: TSLP × IL-13 bispecific monoclonal antibody
Insight: A bispecific antibody, uniquely designed to block both upstream (TSLP) and midstream (IL-13) pathways. May offer synergistic control of Type 2 inflammation.
Competitive Landscape and Market Positioning
Here is a detailed strategic overview of the Competitive Landscape and Market Positioning in Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps (CRSwNP), including approved biologics, leading pipeline therapies, and key companies shaping the future of the treatment paradigm.
Approved Biologics: Market Entrants & Positioning
Drug | Company | MoA | Approval | Key Positioning |
Dupilumab | Sanofi / Regeneron | IL-4Rα antagonist (IL-4/IL-13) | 2019 (US) | First-in-class, broad Type 2 inflammation control; standard of care |
Omalizumab | Roche / Novartis | Anti-IgE mAb | 2020 (US) | Best for allergic endotype patients; second-line |
Mepolizumab | GSK | Anti-IL-5 mAb | 2021 (US) | Eosinophilic inflammation-specific; used with asthma co-morbidity |
These agents revolutionized the treatment of severe CRSwNP in patients uncontrolled by intranasal corticosteroids and surgery. Dupilumab dominates the market due to broader eligibility and superior efficacy data (SINUS-24/52 trials).
Pipeline Therapies: Strategic Innovation Drivers
Upstream Pathway Targeting (next-gen immunomodulation)
Drug | Company | MoA | Phase | Positioning |
Tezepelumab | AstraZeneca / Amgen | Anti-TSLP mAb | III | Broad upstream Type 2 targeting; asthma crossover |
Itepekimab | Sanofi / Regeneron | Anti-IL-33 mAb | III | IL-33 alarmin inhibition; novel target |
Lebrikizumab | Eli Lilly | Anti-IL-13 mAb | III | Focused on IL-13–driven endotype |
Depemokimab | GSK | Long-acting anti-IL-5 mAb | Pre-reg | Designed for less frequent dosing |
Verekitug | Upstream Bio | TSLP receptor antagonist | II | Alternative to TSLP mAbs; smaller biotech play |
CM512/BEL512 | Keymed / Belenos | TSLP x IL-13 bispecific mAb | II (planned) | First-in-class bispecific; dual pathway blockade |
These drugs aim to capture patients with partial/non-response to current biologics or who require broader immune modulation. Tezepelumab and Depemokimab are likely next-to-market leaders.
Regional & Emerging Players (China-centric)
Several Chinese companies are developing IL-4Rα and TSLP-targeting agents as biosimilars or regional competitors to dupilumab and tezepelumab:
Company | Molecule | MoA | Phase |
Sunshine Guojian | SSGJ-611 | Anti-IL-4Rα mAb | III (planned) |
Genrix | Telikibart | Anti-IL-4Rα mAb | III (planned) |
Chia Tai Tianqing | Bosakitug, TQH2722 | Anti-TSLP / IL-4Rα | II |
Jiangsu Hengrui / GSK | SHR-1905 | Anti-TSLP mAb | II |
Keymed Biosciences | CM326 | Anti-TSLP mAb | II (planned) |
These players focus on pricing advantage, regional regulatory acceleration, and biosimilar access. Their global potential depends on differentiation in efficacy, safety, or delivery.
Leading Players & Strategic Advantages
Company | Strengths |
Sanofi / Regeneron | First-mover (dupilumab), large pipeline, IL-33 innovation |
GSK | Expertise in eosinophilic diseases, long-acting IL-5 (depemokimab) |
AstraZeneca / Amgen | Strong TSLP portfolio, leadership in asthma crossover |
Eli Lilly | Focused IL-13 targeting; expanding respiratory biologics |
Keymed Biosciences | Innovative bispecifics, aggressive in Asia markets |
Upstream Bio | Novel receptor-level targeting of TSLP; emerging biotech agility |
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps - Strategic Market Dynamics
- Biologic Expansion: The market is shifting from single-pathway to multi-pathway and upstream targets to improve outcomes in refractory patients.
- Precision Medicine: Endotype-driven drug positioning (e.g., allergic vs eosinophilic) will shape prescription trends.
- Real-World Evidence (RWE): Post-approval studies will heavily influence payor adoption and long-term positioning.
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps - Key Companies:

Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps - Target Opportunity Profile (TOP)
The following Target Opportunity Profile (TOP) comparison table evaluates emerging CRSwNP therapies alongside currently approved biologics, emphasizing key differentiators across efficacy, safety, mechanism of action, route of administration, dosing frequency, therapeutic modality, and innovation potential."
Parameter | Dupilumab (Sanofi/Regeneron) | Omalizumab (Roche/Novartis) | Mepolizumab (GSK) | Emerging Therapies (e.g., Tezepelumab, Depemokimab, Itepekimab, CM512) |
Efficacy | High in Type 2 endotype; broadest real-world use | Effective in allergic CRSwNP | Best for eosinophilic CRSwNP | Aiming for faster onset, higher durability, and broader population |
Target Patients | Broad: Eosinophilic, allergic, AD co-morbidity | Allergic with IgE elevation | Eosinophilic + asthma | Targeting non-responders, non-Type 2, mixed inflammation |
MoA | IL-4Rα blockade → IL-4 & IL-13 inhibition | IgE neutralization | IL-5 inhibition → ↓ eosinophils | Upstream inhibition: TSLP, IL-33, IL-13, bispecifics (e.g., TSLP x IL-13) |
Route of Admin. | Subcutaneous (SC), q2w | Subcutaneous, q2-4w | Subcutaneous, q4w | Mostly SC; some aim for long-acting SC or local delivery (future) |
Dosing Frequency | Every 2 weeks | Every 2–4 weeks | Monthly | Monthly or less frequent (e.g., Depemokimab, q12w potential) |
Safety | Favorable; injection site rxns, conjunctivitis | Generally safe, some anaphylaxis risk | Safe; eosinophil depletion risk | Aiming for equal or improved safety, especially with upstream targets |
Modality | Fully human mAb | Humanized mAb | Humanized mAb | Bispecifics, long-acting mAbs, receptor antagonists (e.g., Verekitug) |
Innovation Level | High at launch; now standard | Moderate; limited in non-IgE endotypes | Moderate; niche | High – new pathways, dual targeting, novel mechanisms |
Endotype Breadth | Strong for Type 2 | IgE-driven allergic only | Eosinophilic only | Aiming for Type 2 + non-Type 2 coverage (e.g., TSLP/IL-33) |
Market Position | Market leader; first-in-class | Second-line for allergic patients | Third-line, niche use | Challengers aiming at superior efficacy, convenience, or new populations |
1. Efficacy
- Superior or broader response across all Type 2 endotypes (including eosinophilic, allergic, and non-allergic patients).
- Faster onset of action (within weeks, not months).
- Greater impact on:
- Nasal polyp score (NPS) reduction
- Sino-Nasal Outcome Test (SNOT-22)
- Time to surgery avoidance
- Ability to demonstrate durability of response post-discontinuation.
Differentiation opportunity: Agents like bispecific antibodies or upstream inhibitors (e.g., anti-TSLP/IL-33) may offer broader, faster, or more durable symptom relief.
2. Safety & Tolerability
- Comparable or lower adverse event rates vs current biologics.
- No increased risk of:
- Hypersensitivity reactions
- Local injection site reactions
- Systemic immunosuppression
- Favorable safety in comorbid asthma, AD, or AERD populations.
Opportunity: Drugs that maintain or improve efficacy while minimizing systemic inflammation risk (especially with upstream targets like TSLP/IL-33).
3. Mechanism of Action (MoA)
- Upstream targeting (e.g., TSLP, IL-33) to modulate broader immune cascades.
- Bispecific or multi-target mechanisms (e.g., TSLP + IL-13) to inhibit multiple pathways.
- Targeting non-Type 2 pathways (e.g., neutrophilic or mixed inflammation) to expand addressable patient population.
Strategic fit: Precision medicine applications and biomarker-based patient selection could maximize differentiation here.
4. Route of Administration (RoA)
- Subcutaneous (SC) remains preferred, but:
- Longer-acting SC (monthly or less frequent) is favorable.
- Intranasal or inhaled formulations may gain favor for local efficacy and lower systemic exposure.
Innovation edge: Depemokimab (long-acting anti-IL-5) offers fewer injections. Nasal delivery remains an underexplored frontier.
5. Dosing Regimen
- Less frequent dosing (monthly or quarterly) is strongly favored.
- Home self-administration capability is a plus.
- Lower total dose burden with comparable efficacy is ideal.
Challenge to beat: Dupilumab’s biweekly dosing. Quarterly or extended-interval biologics could seize share.
6. Modality
- Fully human or engineered antibodies with lower immunogenicity risk.
- Bispecific antibodies, receptor antagonists, or fusion proteins for greater pathway synergy.
- Potential for oral small molecules or gene-modulating therapies in the long term.
Example: CM512/BEL512 (TSLP x IL-13 bispecific) is highly innovative and may unlock synergy.
7. Innovation & Differentiation
- Novel MoAs beyond IL-4/IL-13 axis.
- Strong positioning in patients who fail existing biologics (non-responders to dupilumab).
- Companion diagnostics or biomarker stratification to drive precision use.
- Cross-indication potential in asthma, atopic dermatitis, eosinophilic esophagitis, etc.
Strategic edge: Multimodal biologics with cross-therapeutic potential attract payer interest and support portfolio synergy.
8. Market Access & Value Proposition
- Head-to-head trials or network meta-analyses showing superiority or non-inferiority.
- Demonstrable cost-effectiveness, especially in surgery avoidance or corticosteroid sparing.
- Targeting markets underserved by high-cost biologics (e.g., Asia, Latin America).
Differentiation zone: Emerging biosimilars or region-specific drugs that match efficacy at a lower cost (e.g., Chinese anti-IL-4R agents).
Summary Matrix
Attribute | Must-Have for Competitiveness |
Efficacy | Broad endotype efficacy, durable response |
Safety | Comparable or better tolerability |
MoA | Novel or broader pathway coverage |
RoA/Dose | Monthly or less frequent SC preferred |
Modality | Bispecifics, long-acting mAbs, local delivery |
Innovation | Upstream, dual-target, or failed-biologic responder niche |
Market Fit | Global pricing flexibility, biomarker-based access |
Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps - Strategic Highlights
- Dupilumab sets the benchmark in terms of broad utility, but its q2w dosing and conjunctivitis risk leave room for improvement.
- Emerging therapies such as Tezepelumab (anti-TSLP) and Depemokimab (long-acting anti-IL-5) are leveraging upstream targets and less frequent dosing as key differentiators.
- Bispecific mAbs (e.g., CM512/BEL512) represent next-gen innovation, potentially disrupting the market if efficacy and safety are proven superior.
Why Buy Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report?
Our Pharma Competitive Intelligence Report is designed to give you a strategic advantage by providing deep insights into the pharmaceutical landscape. Here’s how it benefits you and your business: