Global Systemic Sclerosis Market – Industry Trends & Outlook
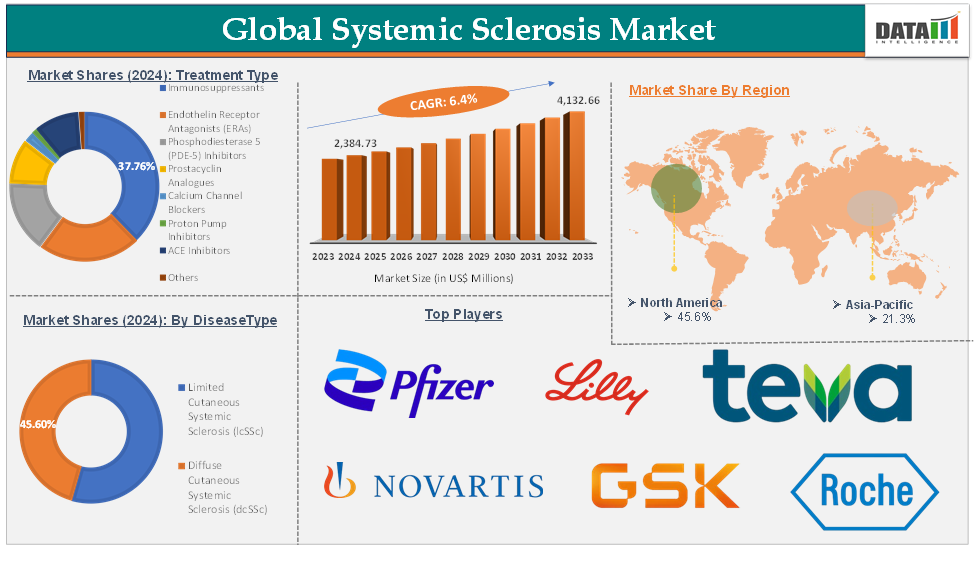
The global systemic sclerosis market was valued at US$ 2,259.64 Million in 2023. The market size reached US$ 2,384.73 Million in 2024 and is expected to reach US$ 4,132.66 Million by 2033, growing at a CAGR of 6.4% during the forecast period 2025-2033.
Systemic sclerosis (SSc), also known as scleroderma, is a rare, chronic autoimmune disease characterized by excessive collagen deposition, leading to skin thickening, organ fibrosis, and vascular abnormalities. Key drivers fueling this market include the rising prevalence of systemic sclerosis worldwide, increasing awareness among healthcare providers and patients, advances in diagnostic techniques, and significant progress in drug development, particularly in immunosuppressants, biologics, and targeted therapies.
Major trends shaping the systemic sclerosis market include a shift toward precision medicine, the adoption of digital health solutions for disease monitoring, growing use of biologics and regenerative therapies, and increased collaboration between biotech firms, pharmaceutical companies, and academic institutions.
Opportunities in this market are abundant, particularly in emerging regions where awareness and healthcare infrastructure are improving, and in the pipeline of new therapies currently under clinical investigation. Government initiatives, orphan drug incentives, and expanded reimbursement policies are also opening doors for innovative treatments and broader patient access.
Global Systemic Sclerosis Market – Executive Summary
Global Systemic Sclerosis Market Dynamics: Drivers
Increasing prevalence of scleroderma
The increasing prevalence of scleroderma is a critical factor driving the growth of the systemic sclerosis market, as it directly correlates with the rising demand for effective diagnostics, treatments, and patient care solutions. For instance, the National Scleroderma Foundation estimates that about 300,000 Americans have scleroderma. About one-third of those people have the systemic form of scleroderma. Since scleroderma presents with symptoms similar to other autoimmune diseases, diagnosis can be difficult. There may be many misdiagnosed or undiagnosed cases.
Localized scleroderma is more common in children, whereas systemic scleroderma is more common in adults. Overall, females with scleroderma outnumber males about 4-to-1. Other factors, such as race and ethnic background, may determine the risk of getting scleroderma, the age of onset, and the pattern or severity of internal organ involvement. The reasons for this are not clear.
Additionally, according to the University of Michigan Health, estimated that systemic sclerosis is the most serious form of the disease. This form of scleroderma can occur at any age but is most common in women of childbearing age. It occurs in around 30 persons per million population per year, and there are an estimated 125,000 active cases in the United States and perhaps 2.5 million worldwide. It is the most fatal of all rheumatologic diseases. Thus, the increasing prevalence of scleroderma serves as a pivotal market driver, propelling advancements in treatment, research, and overall patient care.
Rising advancements in treatment options
Rising advancements in treatment options are a significant driver of the systemic sclerosis market, as they provide new hope for improved management of this complex and often debilitating condition. Historically, treatment for scleroderma was limited to managing symptoms and complications, with few options to directly address the underlying disease mechanisms. However, recent advancements in medical research and technology have led to the development of more targeted therapies, such as biologics, small-molecule inhibitors, and immunosuppressive agents, which can modulate the immune response and reduce fibrosis.
For instance, in March 2024, Cabaletta Bio, biotechnology company focused on developing and launching the first curative targeted cell therapies for patients with autoimmune diseases, stated that, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had granted Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) to CABA-201, a 4-1BB-containing fully human CD19-CAR T cell investigational therapy, for the treatment of systemic sclerosis (SSc). CABA-201 is in development as a potential treatment for autoimmune diseases driven by B cells.
Similarly, in 2024, Certa Therapeutics (Certa), a biotechnology company developing innovative precision therapies for patients with inflammatory and fibrotic diseases, stated that, the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) had granted Fast Track Designation for its investigational therapy FT011 for the treatment of systemic sclerosis (scleroderma), having previously granted Orphan Drug Designation.
Furthermore, advancements in understanding the pathophysiology of scleroderma have spurred the development of drugs targeting specific pathways involved in the disease, such as TGF-beta inhibitors and other antifibrotic agents, which are currently being evaluated in clinical trials. The growing pipeline of these targeted therapies has attracted substantial investments from pharmaceutical companies, further driving market growth.
Global Systemic Sclerosis Market Dynamics: Restraints
The cost of scleroderma treatment is often very high
The high cost of scleroderma treatment is a significant restraining factor for the market, as it limits access to effective therapies and places a heavy financial burden on patients, healthcare systems, and insurers. Treatments for scleroderma often involve expensive medications, such as immunosuppressants, biologics, and antifibrotic agents, alongside supportive therapies, regular monitoring, and management of complications, all of which contribute to the overall cost of care.
For instance, biologic drugs like rituximab, commonly used off-label for scleroderma, can cost upwards of $20,000 to $30,000 per infusion cycle annually, depending on the dosage and frequency required. Additionally, to National Library of Medicine stated that the identified six studies reporting relevant cost estimates were conducted in five different countries, and four studies assessed the humanistic burden of SSc. Total direct annual medical costs per patient for Europe varied from €3544 to €8452. For Canada, these costs were reported to be from Can$5038 to Can$10,673.
In the United States, the total direct health care costs were reported to be US$17,365 to US$18,396. Different key drivers of direct costs were reported, including hospitalisations, outpatients, and medication. The total annual costs per patient were reported at Can$18,453 in Canada and varied from €11,074 to €22,459 in Europe.
Thus, the overall market expansion is restrained, as both patients and healthcare systems grapple with the economic challenges posed by the high cost of scleroderma care, emphasizing the urgent need for more affordable and accessible therapeutic solutions.
Global Systemic Sclerosis Market Dynamics: Opportunities
The development of personalized medicine approaches
The development of personalized medicine approaches offers significant opportunities for the systemic sclerosis market by enabling more precise and effective treatment strategies tailored to individual patients' unique genetic, environmental, and clinical profiles. Personalized medicine allows for the identification of specific biomarkers and genetic mutations associated with scleroderma, which can lead to the development of targeted therapies that address the underlying mechanisms of the disease more accurately than conventional treatments.
By analyzing individual patient data, including genetic information and disease subtypes, personalized medicine can help in predicting disease progression and response to treatment, thus optimizing therapeutic outcomes and minimizing adverse effects. This approach not only enhances the efficacy of treatments but also improves patient adherence and satisfaction by providing therapies that are better suited to their specific condition.
Thus, personalized medicine becomes more integrated into clinical practice, creating opportunities for pharmaceutical companies and researchers to develop and market advanced, tailored treatments that can significantly impact patient care and growth in the systemic sclerosis market.
For more details on this report, Request for Sample
Global Systemic Sclerosis Market - Segment Analysis
The global systemic sclerosis market is segmented based on disease type, treatment type, route of administration, distribution channel, and region.
Treatment Type:
The immunosuppressant treatment type segment is expected to hold 37.8% of the global systemic sclerosis market in 2024
Immunosuppressant treatment is a primary therapeutic approach in the global systemic sclerosis (SSc) market, aiming to control the autoimmune-driven inflammation and subsequent fibrosis that characterize this disease. The most widely used immunosuppressants in SSc include cyclophosphamide, methotrexate, mycophenolate mofetil, and azathioprine.
Cyclophosphamide is particularly effective for SSc-associated interstitial lung disease (SSc-ILD) and is administered either orally or intravenously, typically for up to six months, followed by maintenance therapy with milder agents like methotrexate or azathioprine. Methotrexate is commonly used for skin involvement, while mycophenolate mofetil is favored for both skin and lung disease due to its efficacy and tolerability.
For instance, in December 2024, Zura Bio Limited announced the start of a new global Phase 2 clinical trial called TibuSURE. This study will evaluate the safety and effectiveness of tibulizumab for treating adults with systemic sclerosis (SSc), also known as scleroderma.
Also, in March 2024, Cabaletta Bio announced that the FDA had granted Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) to CABA-201, its investigational cell therapy, for the treatment of systemic sclerosis (SSc), also known as scleroderma. Orphan Drug Designation is a special status provided by the FDA to encourage the development of therapies for rare diseases, offering incentives such as market exclusivity, tax credits, and fee waivers to support research and development efforts. These factors have solidified the segment's position in the global systemic sclerosis market.
Global Systemic Sclerosis Market – Geographical Analysis
North America is expected to hold 45.6% of the global systemic sclerosis market in 2024
The demand for scleroderma treatment in North America is driven by multiple factors such as increasing prevalence, improved diagnosis, rising healthcare expenditure, and ongoing R&D. The scleroderma market in the U.S., Canada, and Mexico has seen growth due to advanced therapeutic options, clinical research, and increased awareness about rare autoimmune diseases.
The U.S. and Canada dominate the North American scleroderma market due to the higher prevalence of the disease. For instance, according to Johns Hopkins University, scleroderma affects many more women than men, and it’s typically found in people between the ages of 30 and 50. As many as 300,000 people in the United States have been diagnosed with scleroderma, and as many as 10,000 die each year from the most serious forms of the disease.
Additionally, according to the NIH (2023, about 17,000 people in Canada have scleroderma, and the disease is 4 times more common among women than men. This higher burden of disease creates a significant demand for effective treatments in the region.
North America, especially the United States, Canada, and Mexico, has robust clinical trial activity. Companies like Cabaletta Bio, Inc., Genentech, and aTyr Pharma, Inc. are heavily investing in clinical trials for drugs aimed at treating systemic sclerosis. The large number of patients enrolled in trials supports market growth.
For instance, in March 2025, the FDA granted Fast Track Designation (FTD) to ADI-001, a genetically engineered T-cell therapy developed by Adicet Bio, for the potential treatment of adult patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc), also known as scleroderma.
Also, in March 2024, Cabaletta Bio announced that the FDA had granted Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) to CABA-201, its investigational cell therapy, for the treatment of systemic sclerosis (SSc), also known as scleroderma. Thus, the above factors are consolidating the region's position as a dominant force in the global systemic sclerosis market.
Asia Pacific is expected to hold 21.3% of the global systemic sclerosis market in 2024
The systemic sclerosis market in the Asia-Pacific region is experiencing significant growth due to several factors, including rising prevalence, increasing awareness, improved healthcare infrastructure, and the introduction of innovative therapies. Countries like China, India, Japan, and South Korea are playing leading roles in the development of this market.
With the increasing prevalence of autoimmune diseases, including systemic sclerosis, there is a growing demand for effective treatments in Asia-Pacific, including China, Japan, and South Korea. Due to the vast population, the potential patient pool for scleroderma is significant. For instance, according to the study conducted by NIH, the pooled prevalence of SSc-ILD in East Asia was 56%. The SSc-ILD prevalence was higher in China (72%) than in Japan (46%) and Korea (51%).
Despite the advancements, awareness of scleroderma remains relatively low in some parts of the region, leading to delayed diagnosis and treatment. Increasing education and awareness programs could further drive market growth. For instance, in August 2024, the National Scleroderma Symposium and Patient Awareness Program, this Symposium intends to provide a unique platform for Rheumatologists and allied professionals from across India to share their experiences, update their knowledge, and interact with each other.
There is an increasing number of clinical trials, including those for autoimmune diseases like scleroderma. Collaborations between pharmaceutical companies and global players, with support from regulatory bodies, are also bringing innovative treatments to the local market. This further boosts the market growth in the Asia-Pacific region.
Global Systemic Sclerosis Market – Competitive Landscape
The major global players in the systemic sclerosis market include Novartis AG, Pfizer Inc., Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, Inc., Eli Lilly and Company, AUROBINDO PHARMA LIMITED, GSK plc, Certa Therapeutics, F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd, Boehringer Ingelheim International GmbH, and Sun Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd, among others.
Global Systemic Sclerosis Market – Key Developments
In February 2024, Certa Therapeutics, a biotechnology company focused on innovative therapies for inflammatory and fibrotic diseases, received Fast Track Designation from the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for its investigational drug FT011 for the treatment of systemic sclerosis (SSc), also known as scleroderma. This follows an earlier Orphan Drug Designation for the same therapy.
Global Systemic Sclerosis Market – Scope
Metrics | Details | |
CAGR | 6.4% | |
Market Size Available for Years | 2022-2033 | |
Estimation Forecast Period | 2025-2033 | |
Revenue Units | Value (US$ Mn) | |
Segments Covered | Disease Type | Limited Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis (lcSSc), Diffuse Cutaneous Systemic Sclerosis (dcSSc) |
Treatment Type | Immunosuppressants, Endothelin Receptor Antagonists (ERAs), Phosphodiesterase 5 (PDE-5) Inhibitors, Prostacyclin Analogues, Calcium Channel Blockers, Proton Pump Inhibitors, ACE Inhibitors, Others | |
Route of Administration | Oral, Parenteral | |
Distribution Channel | Hospitals, Pharmacies, Retail Pharmacies, Online Pharmacies | |
Regions Covered | North America, Europe, Asia-Pacific, South America, and the Middle East & Africa | |
The global systemic sclerosis market report delivers a detailed analysis with 70 key tables, more than 65 visually impactful figures, and 173 pages of expert insights, providing a complete view of the market landscape.