Sickle Cell Disease (SCD) is one of the most common inherited blood disorders worldwide, affecting millions of people, especially those of African, Middle Eastern, and Mediterranean descent.
Despite its history as a neglected disease, recent breakthroughs in drug development, therapies, and innovations are providing hope to patients and caregivers. The emergence of new treatments is beginning to reshape the SCD landscape, transforming what was once a disease with limited options into one where targeted therapies and precision medicine are increasingly taking center stage.
Key Players and Therapies in the Sickle Cell Landscape
Historically, pain management and blood transfusions have been the primary treatments for SCD, with a focus on managing the symptoms rather than addressing the underlying cause of the disease. However, in the past decade, a series of innovative drugs have been introduced, offering more effective treatments with the potential for long-term relief.
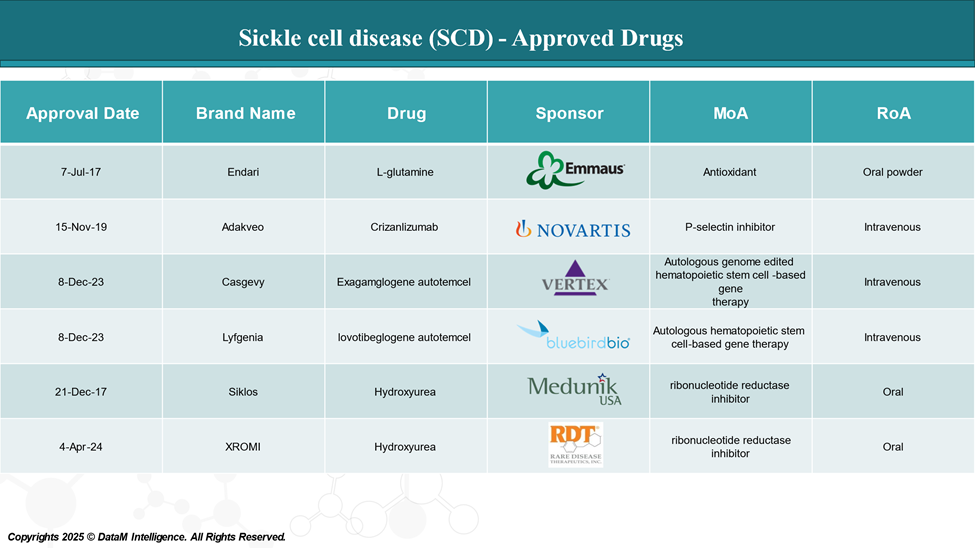
Hydroxyurea (Hydrea®)
- Company: Bristol Myers Squibb/CHEPLAPHARM ARZNEIMITTEL GMBH
- Mechanism: Chemotherapy agent that increases fetal hemoglobin (HbF) production, which helps reduce the sickling of red blood cells.
- Current Use: Standard of care for patients with moderate to severe SCD.
- Key Benefit: Hydroxyurea can reduce the frequency of painful episodes, decrease hospitalizations, and improve overall quality of life.
Endari® (L-glutamine)
- Company: Emmaus Life Sciences
- Mechanism: Amino acid that reduces oxidative stress and improves red blood cell function.
- Current Use: Approved for the treatment of sickle cell-related complications in patients aged 5 years and older.
- Key Benefit: Reduces the frequency of sickle cell crises.
Crizanlizumab (Adakveo®)
- Company: Novartis
- Mechanism: Monoclonal antibody that targets P-selectin to reduce cell adhesion and prevent sickling.
- Current Use: Approved for adults and pediatric patients with SCD.
- Key Benefit: Reduces the frequency of vaso-occlusive crises (painful episodes).
Gene Therapy and Editing (Exagamglogene autotemcel)
- Company: CRISPR Therapeutics and Vertex Pharmaceuticals
- Mechanism: Gene-editing approach that uses CRISPR technology to modify the patient’s own cells to produce high levels of fetal hemoglobin.
- Current Use: treatment of patients aged 12 years and older with sickle cell disease (SCD) with recurrent vaso-occlusive crises (VOCs).
- Key Benefit: Potential for a one-time, curative treatment.
Innovative Trends Shaping the Future of Sickle Cell Disease Treatment
The SCD treatment landscape is rapidly evolving, and several key trends are defining the direction of research, development, and patient care:
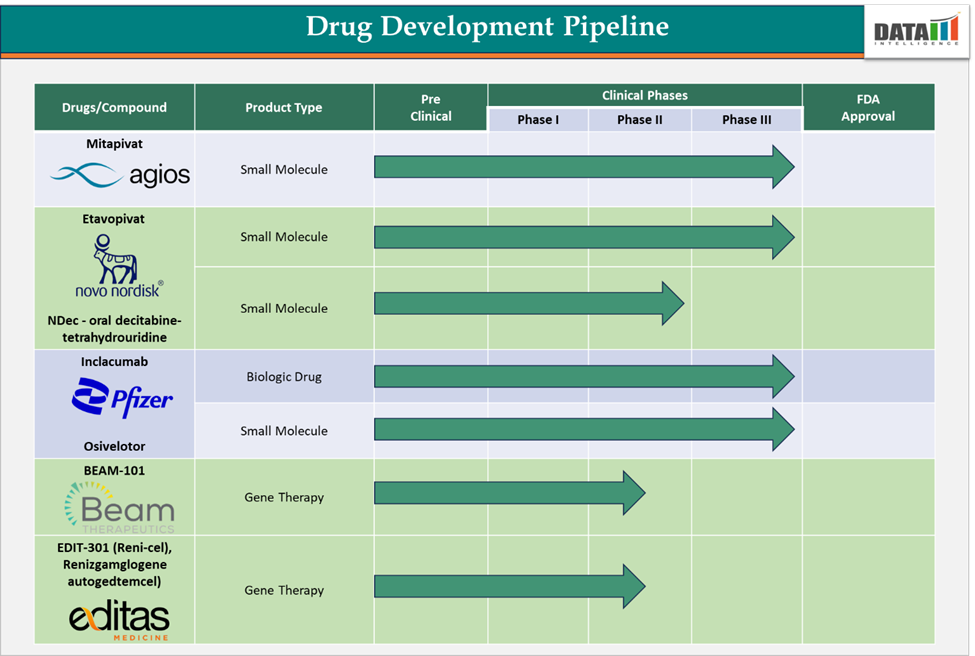
- Gene Therapy and Genome Editing
The approval of gene therapies like Exagamglogene autotemcel is arguably the most exciting advancement in the SCD field. By directly modifying the genetic material in a patient’s own stem cells, these therapies hold the potential to cure SCD by enabling the production of functional hemoglobin.
- Combination Therapies
As companies move beyond single-drug treatments, the trend toward combination therapies is gaining traction. For example, combining Voxelotor with Crizanlizumab or hydroxyurea may help to increase treatment efficacy and reduce the frequency of sickle cell crises. This approach could offer patients a broader, more robust treatment regimen that addresses multiple aspects of SCD.
- Personalized Medicine
Advancements in genomic profiling and biomarker identification are making it possible to develop personalized treatment strategies for SCD patients. By understanding the genetic and molecular makeup of a patient’s disease, clinicians can tailor therapies that are more effective and safer.
Improved Access to Treatment
Despite the impressive advancements, many patients still struggle to access the latest therapies due to economic and geographical barriers. Efforts are underway to improve access through global initiatives, partnerships, and programs aimed at providing affordable care and ensuring patients can receive life-changing therapies.
What Lies Ahead for Sickle Cell Disease
As drug development accelerates and innovative treatments become more accessible, the future of Sickle Cell Disease treatment looks promising. The industry is experiencing an explosion of therapeutic options, from gene therapies offering potential cures to innovative drug combinations that can improve patient outcomes.
For patients and caregivers, this new era brings hope — hope for not just managing the symptoms of SCD, but for transformative, long-term solutions that could ultimately cure the disease.
As research progresses and new therapies emerge, the SCD treatment landscape will continue to evolve rapidly. Keeping an eye on the key players, emerging trends, and clinical trial developments will be crucial for anyone involved in the care or study of this complex and devastating disease.
